Mastering module scripting is an essential part of becoming a developer. Roblox Successful. These easy-to-use script shortcuts are useful for coding common game elements, such as money, rewards, and enemy interactions. Using them saves a lot of time when writing code for your creations. Roblox Yours. Module scripting may seem confusing at first, but this guide will explain why and how to use module scripting in Roblox.

Roblox Module Script Basics
Before learning how to use module scripts and link them to other scripts, it's important to have a basic understanding of them. In simple terms, module scripts are parts of a script. They are used to store functions, variables, and other pieces of code.
However, the key characteristic of a module script is that it cannot run on its own or do anything on its own. Instead, it must be called or accessed by other scripts. It's almost like a reference that other scripts or other pieces of code can call upon to get the information they need for a particular function.
In terms of use and purpose, module scripts are typically used to store functions that appear frequently in your game. For example, many games include money or rewards that are given to the player for performing certain tasks, such as defeating enemies or completing missions.
A module script can be used to store the function and related data to reward the player. Later, when you write other scripts about fighting enemies or going on adventures, you can call the module script to retrieve the data you need.
Create a module script in Roblox
Here's how to add a script to Unity in a few quick steps:
- Go to the tab “Model” in RobloxStudio.
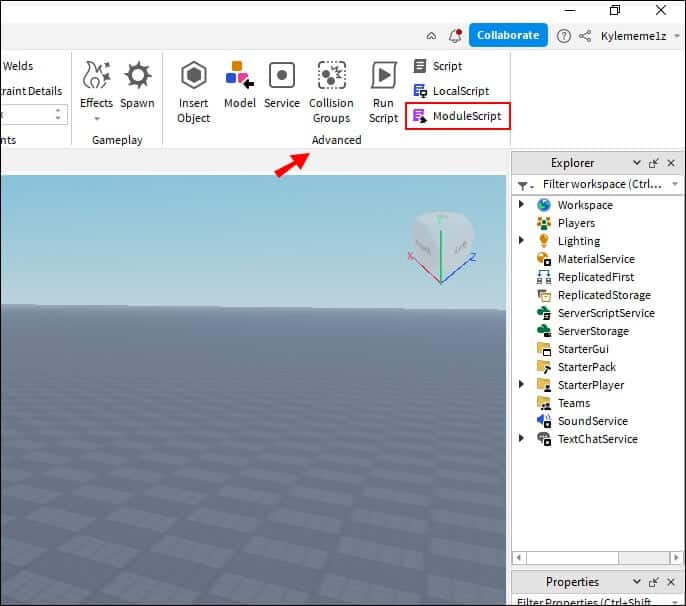
- Search for a department "advanced" In the upper left. Click on purple button Named “Module Script”.
- A new Unity script will open in your workspace, ready for you to modify as you see fit.
Roblox Module Scripting Structure
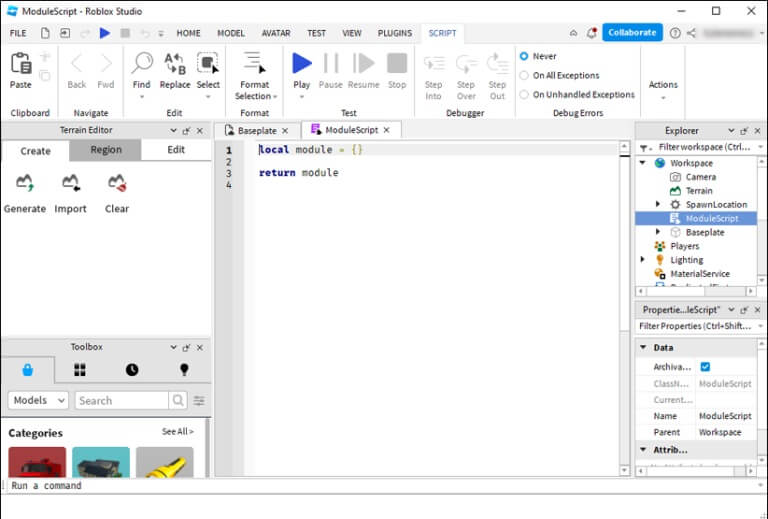
When you first add a script to the module, this is what it will look like:
local module = {}
return module
This is the basic structure of all module scripts. There are only two main lines. The first is used to create tables and store functions and variables, while the second line "The Return" It is the part that allows other texts to draw information from the unit.
Of course, as you edit and add scripts to your module, they can become longer and more complex, but the two basic lines will always exist and remain mostly unchanged. Any data you choose to add should flow between them.
Rename module scripts
Before you do anything else with your unit script, you'll likely need to rename it. You may end up with dozens of unit scripts as your game evolves, so it's helpful to give each one a convenient, easy-to-understand name to simplify things for you.
Let's imagine you're setting up a module that rewards players with coins, for example. You might choose a self-explanatory name like “CoinReward” Then add it to the module script instead of the word “module”, which gives you the following:
local CoinReward = {}
return CoinReward
Add to module scripts
With just two lines of code, module scripts aren't going to be very useful. You'll need to add more data to make them useful and worthwhile. There are all sorts of ways to customize your module scripts. But the two main additions people tend to make are variables and functions.
To add a variable, type the name of your module, followed by a period, then the name and relevant data for your variable, like this:
local CoinReward = {}
CoinReward.Variable = 100
return CoinReward
To add a function, you need to write "function" , followed by the name of your module and the relevant code for your function. For example, if we wanted to add a function to award a player a coin reward, it could begin like this:
local CoinReward = {}
function CoinReward.GetCoins
return CoinReward
You can then add the necessary additional lines of code to create parameters for how the player will receive coins, how much they will get, whether there are any modifiers, etc.
Calling modules from other scripts
The important thing to remember about module scripts is that they don't do anything on their own. They can't run code independently. Instead, they store code and functions that other scripts can call from. This is done using the "require()".
For example , "require()It allows another script to look up information from a module script, and you can use it simply by adding it as a variable in the script you want to work with. For example:
local CoinReward = require(ServerStorage.CoinReward)If you use the line above, your script will be able to load information from the CoinReward module script you created earlier. You can then go deeper, implementing several additional functions and variables to make your module script more useful, and using the require() function to add it to other scripts.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: Do I need to use module scripts?
The answer: You don't technically have to use module scripts, but they are a convenient and effective part of Roblox scripting. They can help you organize your code in several different ways and reuse the same functions multiple times without having to rewrite the same piece of code. If you want to create complex and in-depth games more quickly and easily, mastering module scripts will definitely help.
Q2: Are module scripts complex?
The answer: They can. Some developers, especially those new to Roblox Studio, may find them difficult to understand at first. Others, especially seasoned programmers, don't have much trouble working with them. Even if you find them confusing at first, practice should help, and there are plenty of video tutorials and guides to follow to guide you through the first module's scripts.
Q3: Why is my module script not working?
The answer: If you see an error like “Invalid Number,” you may have made a typo. Even a simple typo in your module script name can make it impossible to connect from. Take a close look to make sure the names match across all your scripts. If there’s no typo, another coding error may be causing the problem. For example, your script might be missing “require()".
Q4: Where do I put my code in a module script?
Answer: All code you want to add to a module script must be enclosed between the “local module = {}"The first line"return moduleDo not try to add anything before or after these two fields, as this may cause confusion and lead to errors that are difficult to resolve.
Main unit manuscripts
If you're just getting started with scripting, Roblox Module scripts may seem challenging. However, it's highly recommended that you explore them and make them part of your coding skill set. Once you've learned the basics and created your first module script, it should become easier to accomplish more and reap the rewards, saving you a lot of time and keeping your code organized and under control.
Have you used module scripts a lot in Roblox Studio? Do you have any helpful programming tips and tricks to help beginners? Share your wisdom and thoughts in the comments below.