File recovery tools are among the most important programs in a Linux administrator's toolkit. They provide the ability to recover deleted files on Linux, even if the disk is physically damaged or erased.
When you delete a file, only the association between it and its underlying data is removed. The physical file itself remains intact. It simply tells the operating system that space is now available for overwriting.
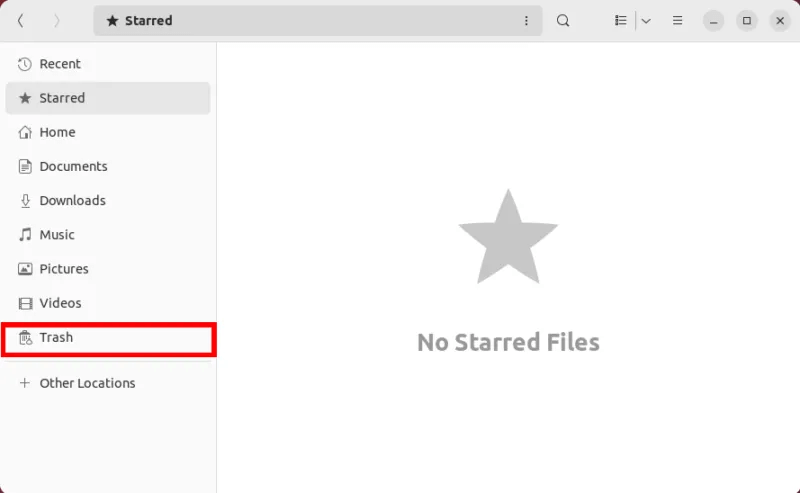
Additionally, most desktop environments today prevent you from directly deleting files on your disk. Instead, they move the deleted file to the Trash folder (or Recycle Bin in Windows), from where it can then be easily recovered.
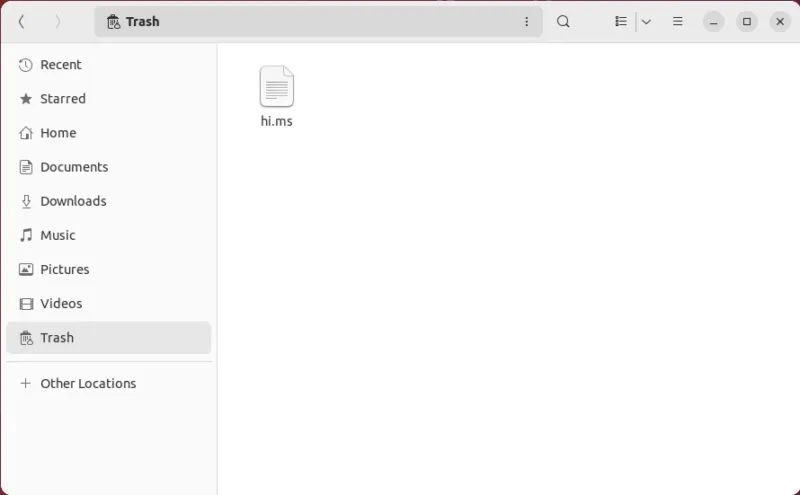
You can recover your files in Linux by accessing the Trash folder on your desktop.
- Click on Win , then type "Files".
- Click Enter “trash” On the left sidebar of the file manager.
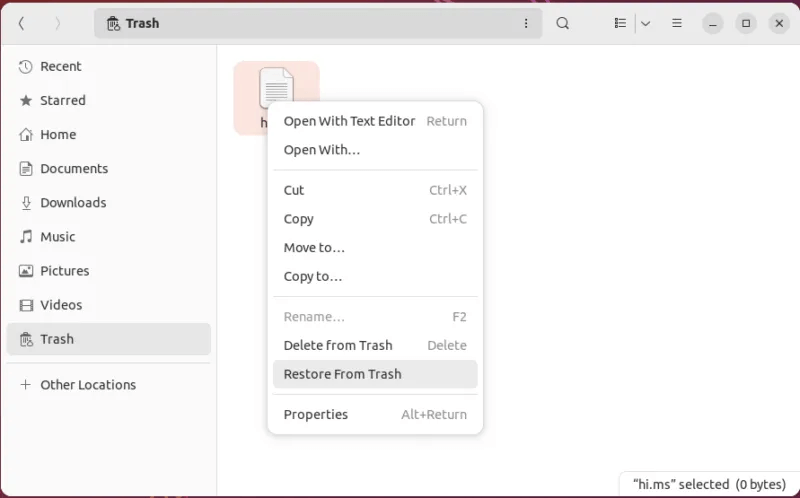
- Right click File which you want to recover and select "Recover from Trash".
Tip: You can also make sure the file is unrecoverable by: Proper secure deletion procedure.
1. Testdisk
Testdisk It's one of the most popular deleted file recovery tools on Linux. It's a powerful terminal program that can recover lost partitions from virtually any disk. It works by browsing each cylinder on your disk while searching for any partition table data.
This means that Testdisk can restore the file system even after it has been wiped clean. This can also be useful in cases where you accidentally formatted a disk and deleted its internal partition table.
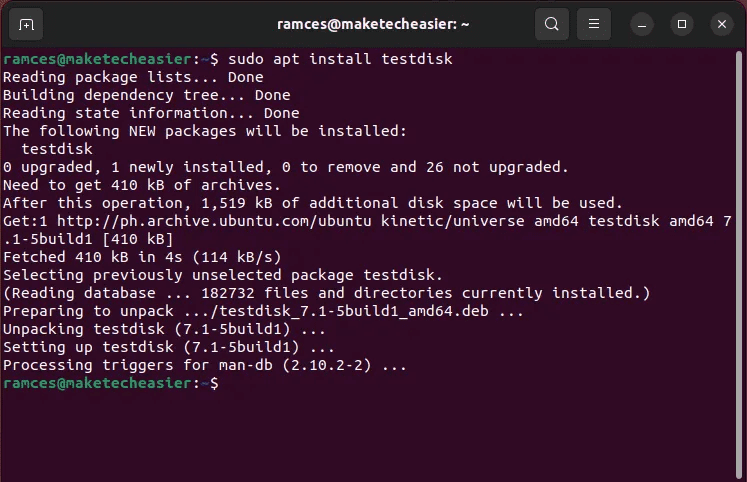
- Install Testdisk on Ubuntu and Debian by running the following command:
sudo apt install testdisk
- Enter
sudo testdiskIn your terminal window to run the program.
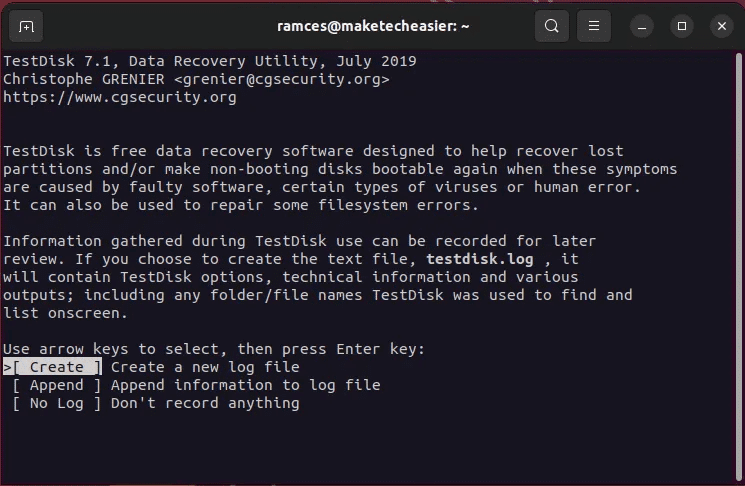
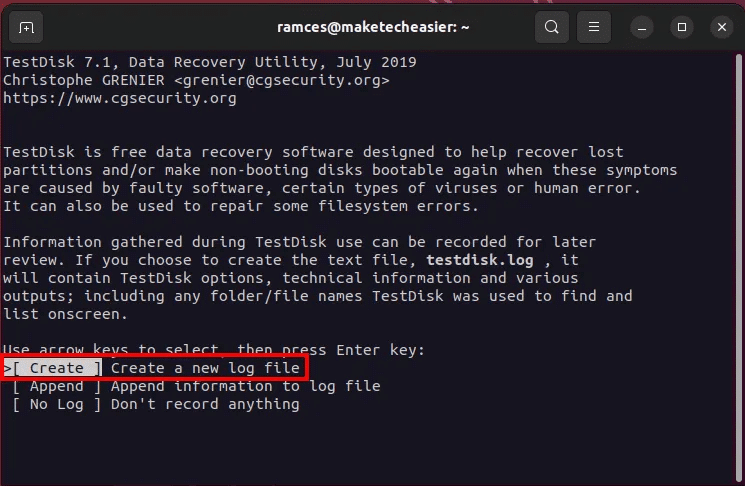
- Locate "construction" To tell Testdisk that you want to store the current session log.
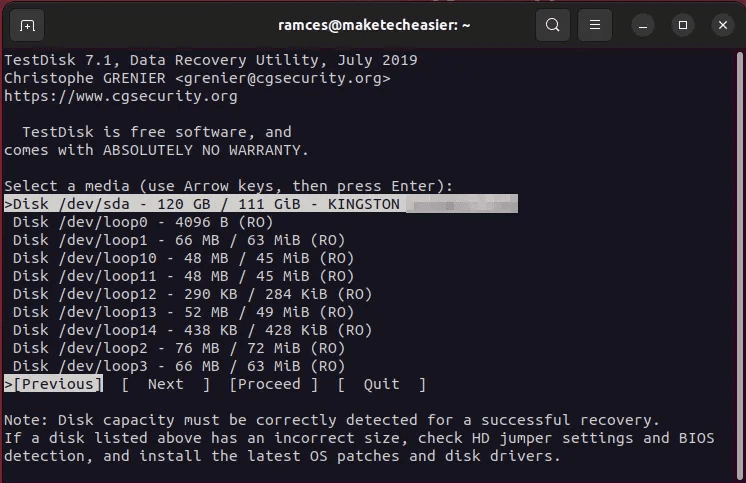
- Locate disc which you want to recover. In my case, it's “/dev/sda.”
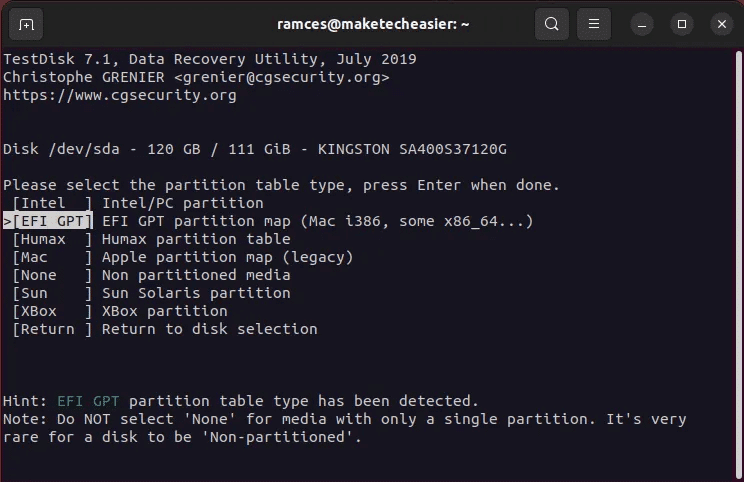
- Locate Partition table type For your disk.
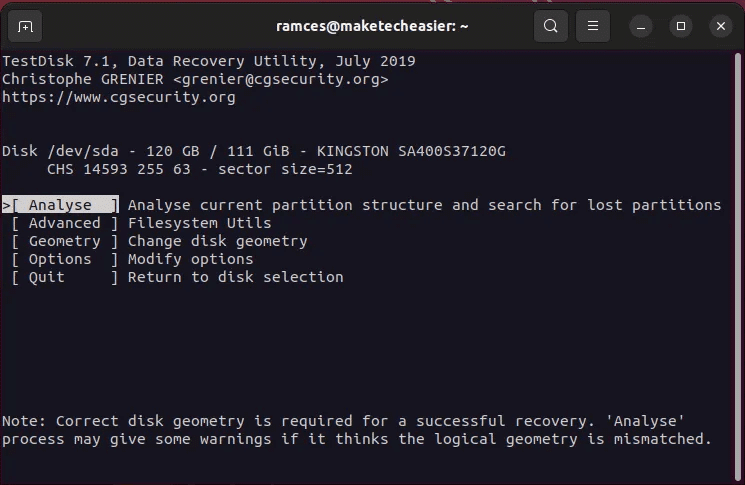
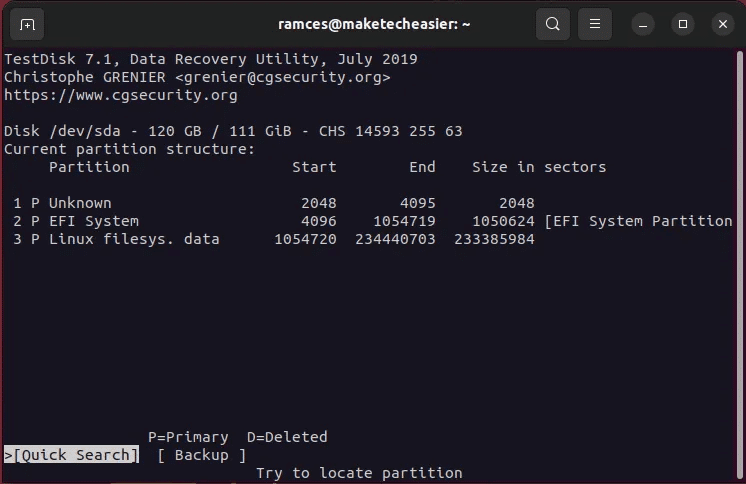
- Locate "analysis" To check the disk for any inconsistencies with Current section layout.
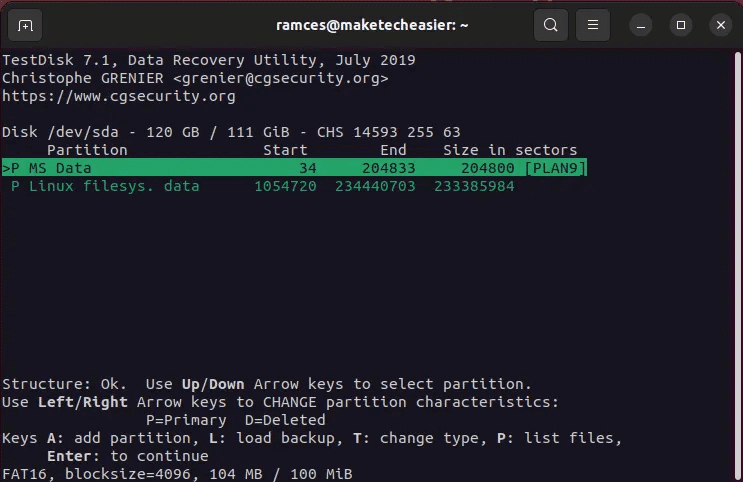
- Select an option Quick search To start the process Retrieve section.
- Click on Enter To accept default values for Test disk.
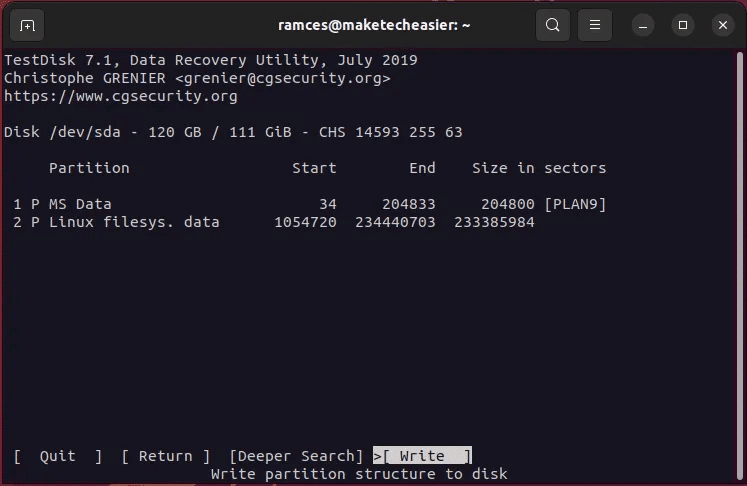
- Locate "Writing" To save the new section layout.
Positives
- Recovers entire disk partitions
- Repairs disks with unbootable operating system
Negatives
- Individual files cannot be recovered.
- Restoring the partition will not guarantee that its contents are still there.
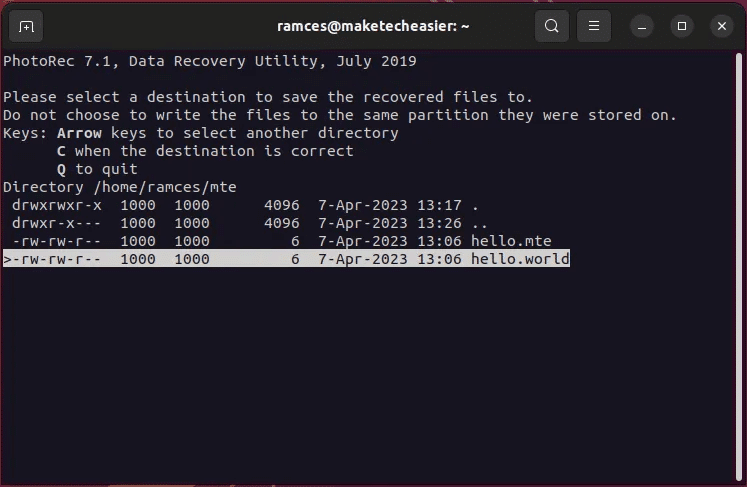
2. Photorec
Photorec It's a simple tool that can recover files through data scraping in Linux. It's a process in which the program reads the raw bytes of a disk to find the contents of a deleted file.
One of the biggest advantages of Photorec is that it is often bundled with the Testdisk package. You don't need to install any additional utilities or dependencies to begin file recovery.
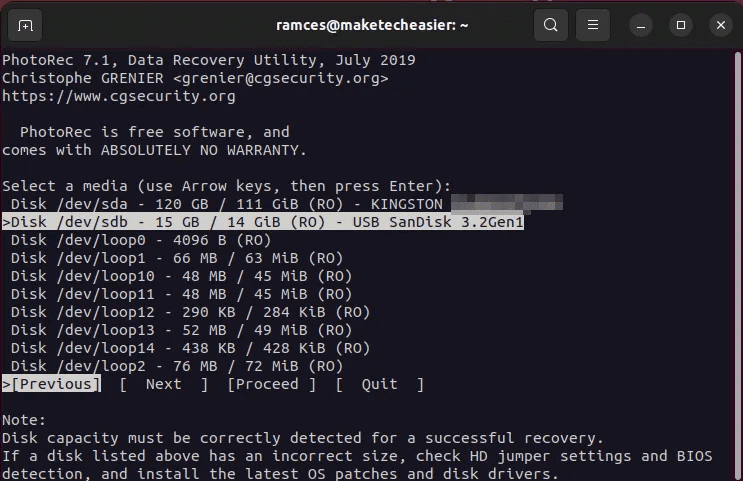
- start in Recover your data By running photorec:
sudo photorec
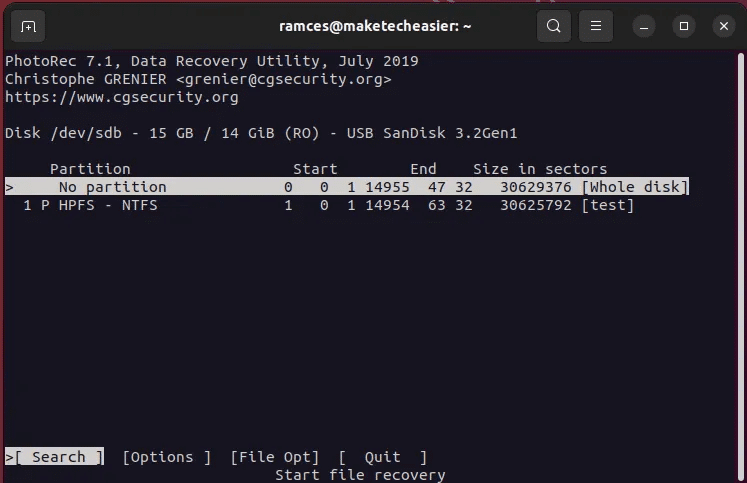
- Highlight the disk that contains the files you want to recover, and then select "Continue".
- Select the option “[The entire disc]”, Then press Enter.
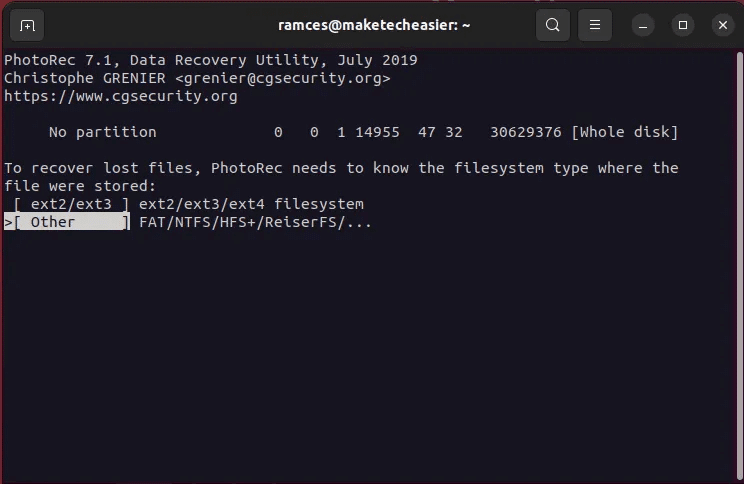
- Select the file system that initially saved the deleted file.
- Provide Recovery Guide For Photorec. To select one, go to Guide Target using arrow keys , then press C.
Positives
- Fast recovery algorithm
- Handles a variety of file system formats.
Negatives
- Recovery can penalize solid-state drives.
- Requires a separate file system to store files.
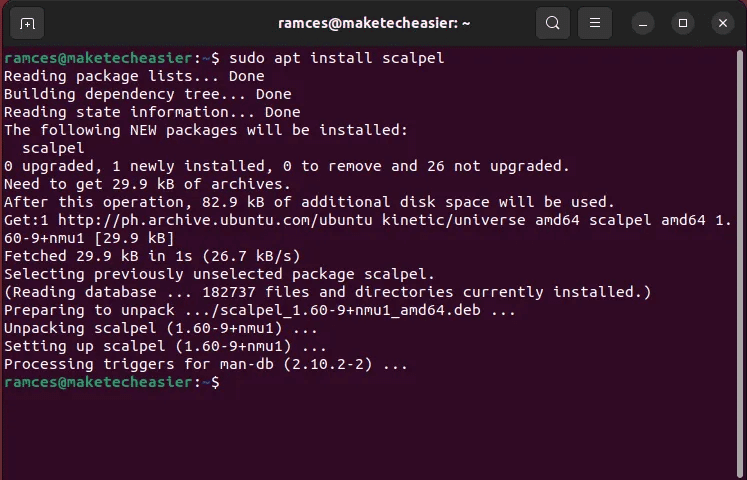
3. Scalpel
Scalpel It's a fast and efficient program that uses regular expressions to recover any lost files on a Linux disk. Similar to Photorec, Scalpel scans your disk and looks for any byte patterns that could indicate existing data.
One of the features of Scalpel is that you can use regular expressions to fine-tune what the program will recover, so it only takes a fraction of the time compared to similar programs.
- install Scalpel In Ubuntu and Debian by running the following command:
sudo apt install scalpel
- Copy the default configuration file for Scalpel To your home directory:
cp /etc/scalpel/scalpel.conf /home/$USER/
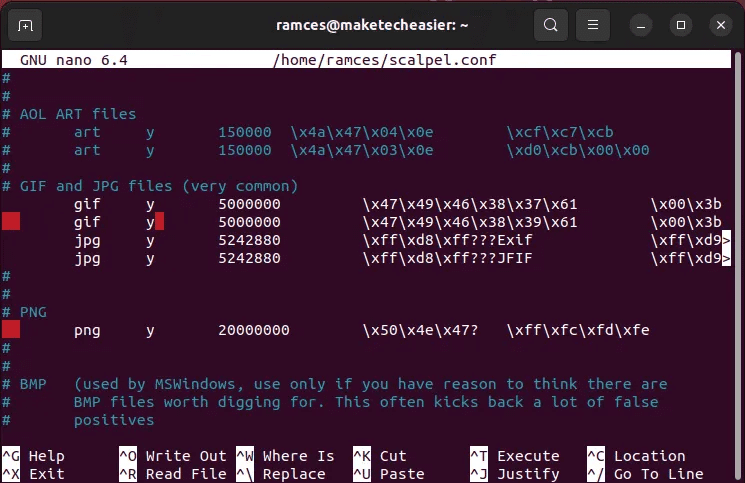
- open file scalpel.conf Through your text editor:
nano /home/$USER/scalpel.conf
- Uncomment lines containing File Extensions that you want to recover.
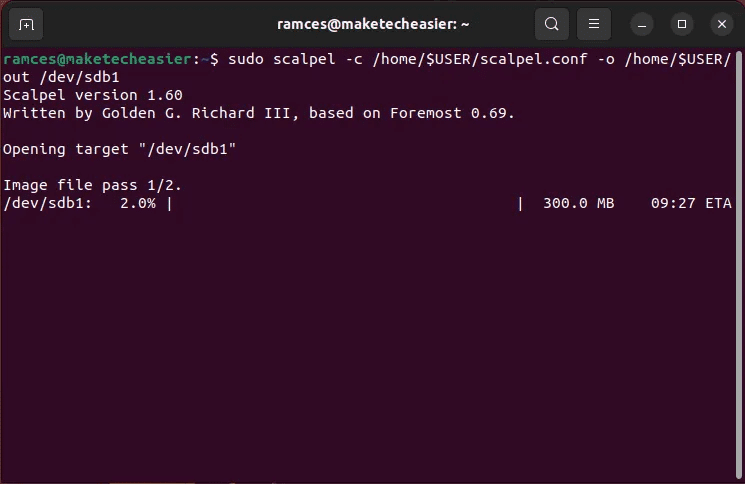
- turn on Scalpel Using the following command:
sudo scalpel -c /home/$USER/scalpel.conf -o /home/$USER/out /dev/sdb1
Positives
- Works on both device files and disk images.
- Allows you to filter the type of file you want to recover.
Negatives
- The configuration file can be confusing.
- It can be unreliable in detecting file types.
4. ddrescue
ddrescue It is a powerful data recovery utility that uses intelligent algorithms to preserve the entire contents of disk devices. Unlike data transfer tools, ddrescue's primary goal is to recover and preserve data as accurately as possible.
By design, ddrescue doesn't extract files from the disk in this way. Instead, it creates a "snapshot" of the disk's current state, which can be useful when you're extracting data from a failing hard drive.
- You can install ddrescue In Ubuntu and Debian by running the following command:
sudo apt install gddrescue
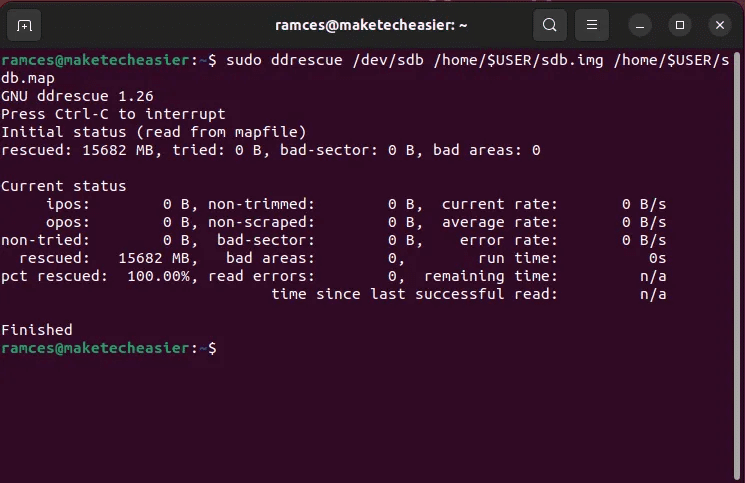
- Start preserving the contents of your disk. For example, the following command will create an image file from the disk device: “/dev/sdb”:
sudo ddrescue /dev/sdb /home/$USER/sdb.img /home/$USER/sdb.map
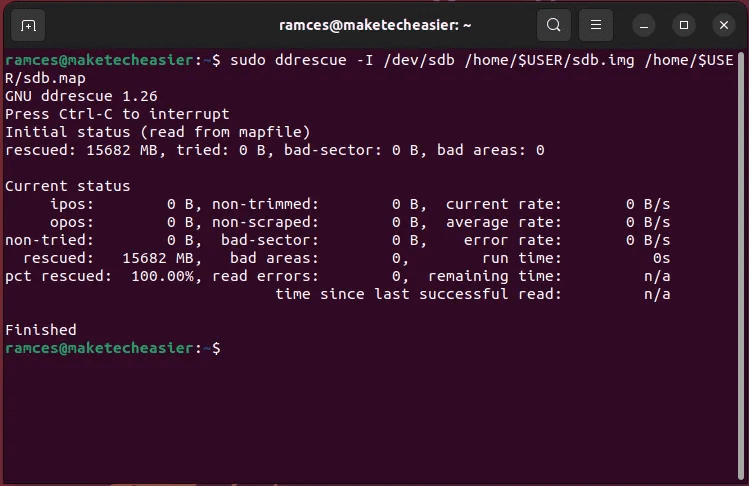
- Verify the integrity of your shot with the tag.
-I:sudo ddrescue -I /dev/sdb /home/$USER/sdb.img /home/$USER/sdb.map
Positives
- Creates an exact copy of your disk.
- Skips bad sectors on the hard disk
Negatives
- It will not recover a lost file directly.
- It can be slow on large hard drives.
5. Fatcat
Fatcat Fatcat is a lightweight program that can recover files within FAT file systems on Linux. This includes the older FAT12 format and even the newer FAT32. Fatcat can be a great tool for recovering data from older hard drives.
One of Fatcat's best features is that it can be used as a portable file explorer for FAT drives. You don't need to extract an image file to access and recover its contents.
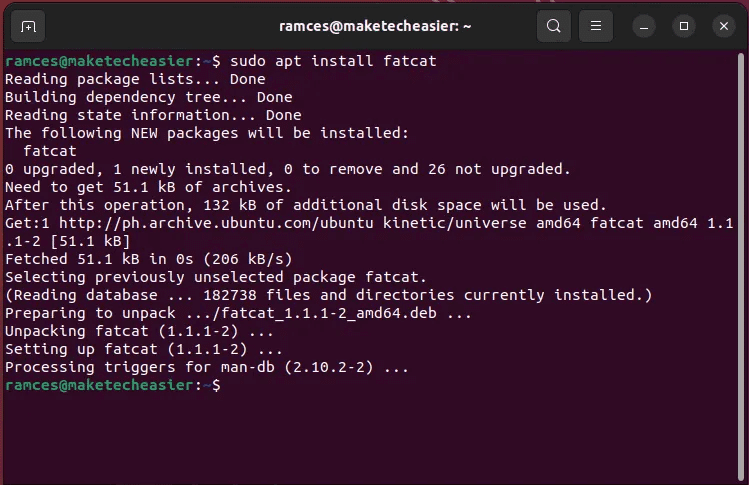
- install Fatcat In Ubuntu and Debian by running the following command:
sudo apt install fatcat
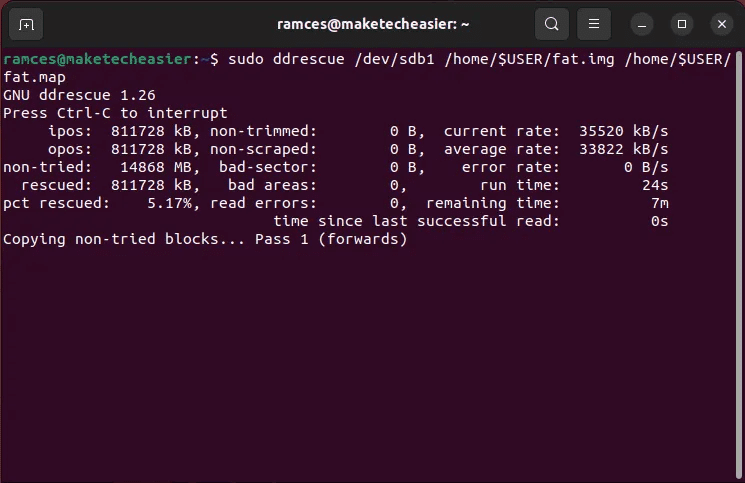
- Create FAT partition image file your using ddrescue:
sudo ddrescue /dev/sdb1 /home/$USER/fat.img /home/$USER/fat.map
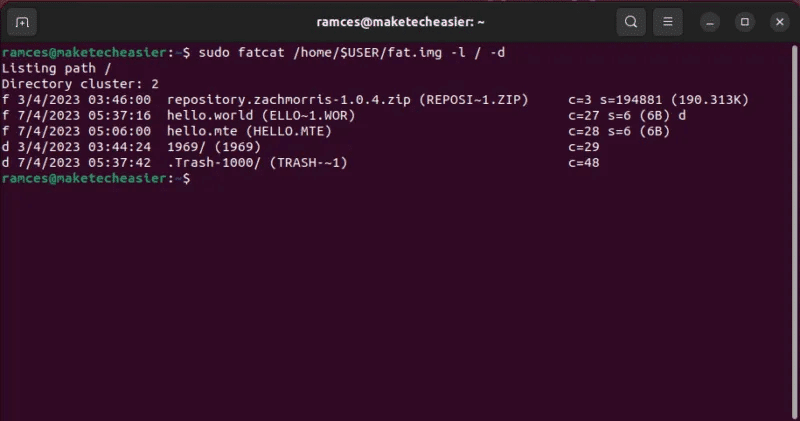
- Verify FAT image contents Your own by listing its root:
sudo fatcat /home/$USER/fat.img -l / -d
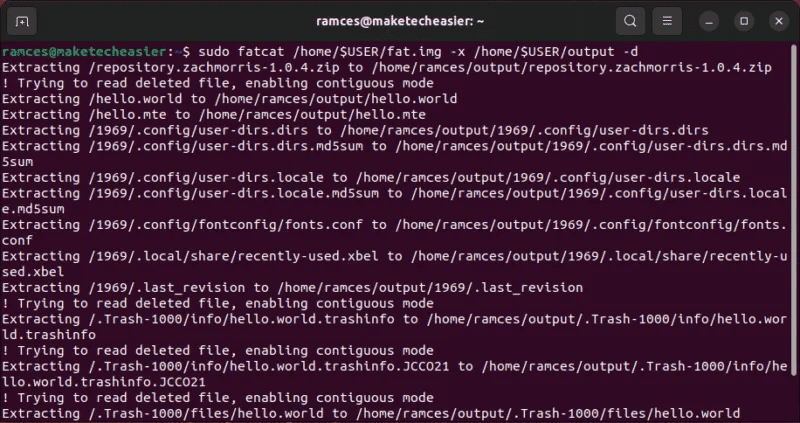
- evacuation FAT partition contents In your file system:
sudo fatcat /home/$USER/fat.img -x /home/$USER/output -d
Positives
- Loads FAT partition contents at super fast speed
- Repairs broken FAT file systems
Negatives
- exFAT is not supported.
- Recovering individual directories can be difficult.
6. Ntfsundelete
Ntfsundelete It is a tool that can repair and recover files in NTFS file systems on Linux. Similar to Fatcat, Ntfsundelete can recover individual files as well as entire directories and disks.
Ntfsundelete is present in most Linux distributions by default, where it is included in the ntfs-3g package that acts as a compatibility layer for NTFS on Linux.
- Create an image file of your NTFS partition using ddrescue:
sudo ddrescue /dev/sdb1 /home/$USER/ntfs.img /home/$USER/ntfs.map
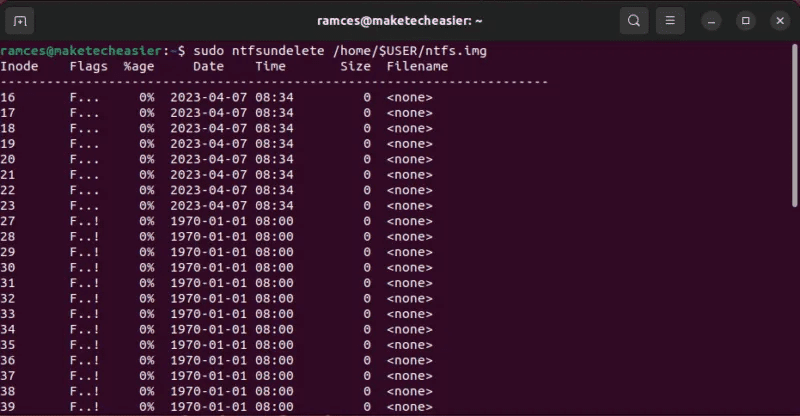
- Test the consistency of your image file by listing its contents:
sudo ntfsundelete /home/$USER/ntfs.img
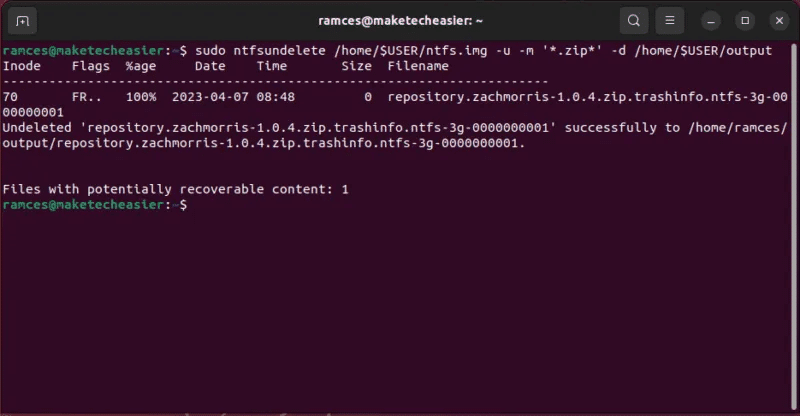
- Recover data from your disk image. For example, the following command will recover all ZIP files from the disk image:
sudo ntfsundelete /home/$USER/ntfs.img -u -m '*.zip*' -d /home/$USER/output
Positives
- A core part of most Linux distributions.
- Recovers individual files
Negatives
- Unreliable with device files
- The names of the recovered files may differ from the original.
7. Ext4magic
Apart from recovering files within FAT and NTFS partitions, it is also possible to recover files from the Linux Ext file system. Ext4magic A powerful software that can undelete almost any file from Ext3 or Ext4 file system.
One of Ext4magic's selling points is that it can recover files using date ranges. This can be useful in situations where you can't remember the exact file name and original file type.
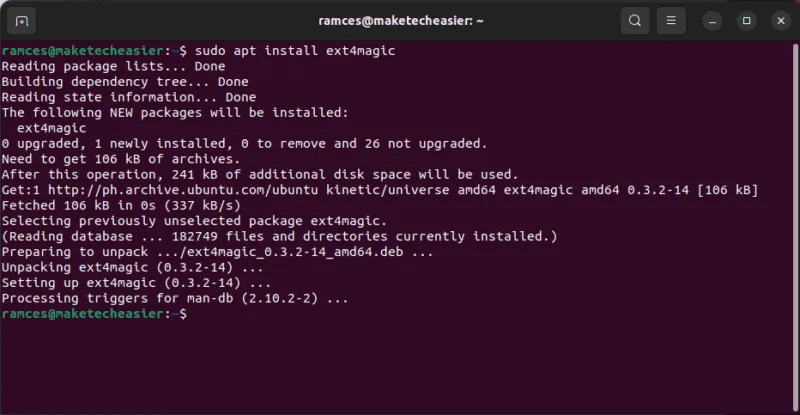
- install Ext4magic In Ubuntu and Debian by running the following command:
sudo apt install ext4magic
- Create disk partition image Your using ddrescue:
sudo ddrescue /dev/sdb1 /home/$USER/ext.img /home/$USER/ext.map
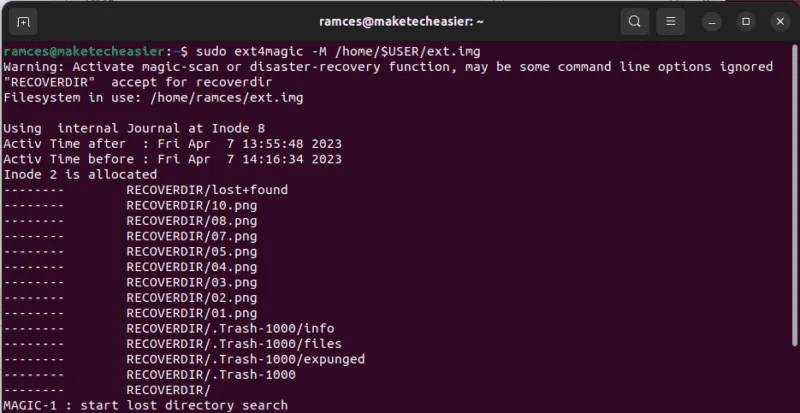
- Recover deleted files with ext4magic. For example, the following command will recover all files on my Ext4 disk:
sudo ext4magic -M /home/$USER/ext.img
Positives
- The journal file is used to help recover files.
- Scans the file system for problems.
Negatives
- The time range option uses the UNIX epoch format.
- It can be unreliable with older deleted files.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What can I do if Photorec still can't find my file after scanning?
The answer: In some cases, Photorec's first recovery pass may lose some important bytes of data. To fix this, select the "Deep Scan" option after the first pass to tell Photorec to rescan.
Q2. Is it acceptable to enable all file extension filters in Scalpel؟
The answer: Yes. However, it will reduce the effectiveness of Scalpel, as some file format entries in "scalpel.conf" can produce many false positives. It is good practice to enable only the options you need for a particular scan.
Q3. Why can't I open my FAT image file with Fatcat?
The answer: This is most likely due to a mismatch between the image file and the format expected by Fatcat. To fix this, run ddrescue on the partition with the FAT file system instead of the entire disk.