It's a great idea to log into your SSH server without a password. Seriously, get rid of it. There's no need to use a password on one of the most vulnerable services on Linux servers, right? Securing the SSH server Using standard password-based authentication is a bad idea. Attackers can easily crack passwords, and when they're the only thing standing between a bad actor and your server, you should definitely be nervous. That's why RSA key-based authentication is much better. You can configure and secure your Linux server to only allow access from computers with already accepted RSA keys. Anyone else will be instantly rejected. As an added bonus, you can generate these keys with or without a password—it's entirely up to you. However, a strong key without a password is a good idea in most cases. In this guide, we'll walk you through how to enable passwordless SSH logins on Linux.

If you also use Linux machines at home, you have the added benefit of convenience. Let's say you want to set up SSH X forwarding from your Linux workstation to your laptop. Do you really want to have to enter your password every time you launch a remote program? Set up SSH keys, and you won't have to.
Install packages
There are a few packages you need. You probably already have some of them, but it's a good idea to double-check them. The packages are the same on both the server and the client. However, there's also a good chance that both machines are servers and clients to each other (home mode), so you might want to make sure you have these packages installed.
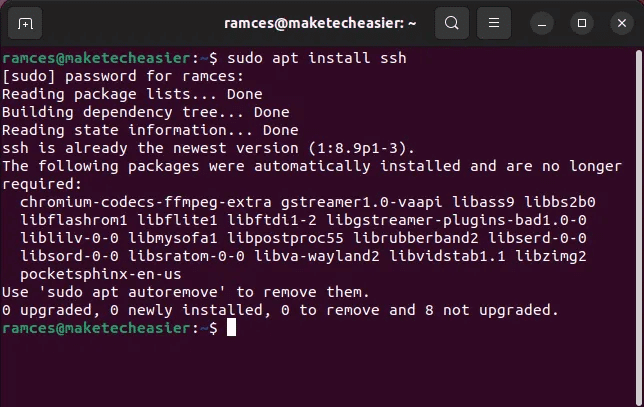
The OpenSSH metapackage is not installed by default on systems. Debian Or UbuntuIf you don't already have it installed, you can do so by running the following command:
sudo apt install ssh
Create your own SSH key in Linux
It's really easy. Create an SSH key On Linux, simply tell OpenSSH that you need to generate the key. It's also a good idea to specify the number of bits with the -b flag and the type with -t. A 4096-bit key is best, as it provides stronger encryption.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519
First, the tool will ask where you want to store the key. Just tap Enter For the default directory. When prompted for a password, leave it blank for a passwordless key and passwordless authentication. If you want to use a password for your key, enter it here.
Your computer will take a few seconds to generate your key. When it's finished, it will print an ASCII representation of your key on the device.
Send your key to a remote Linux host
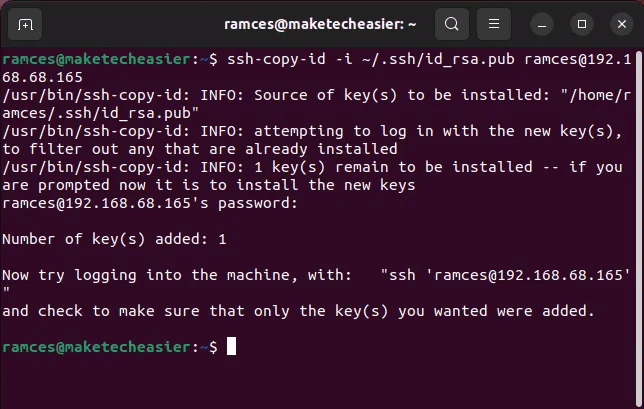
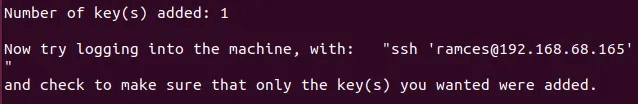
To use your key, you'll need to send it to your remote server. OpenSSH has another built-in tool for that as well. Tell it where your key is and which user on the server to bind it to.
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub username@ip_remote_host
replace ip_remote_host with the actual IP address of the remote host, which you will be managing via SSH. Replace username with the actual username on the remote host.
It is necessary to use the -i option to specify the identity file that contains your public key. If you try to use an SSH key without this option, you may get an error.
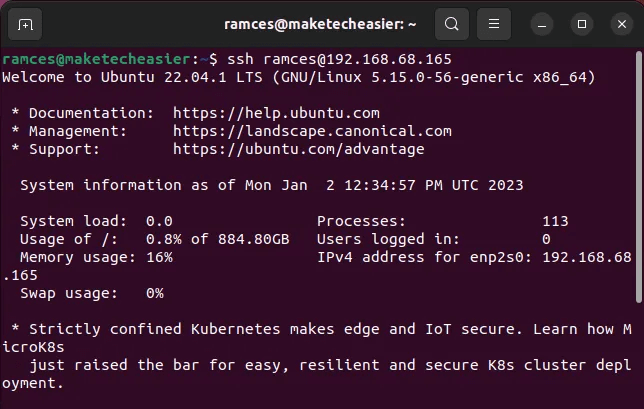
Testing your SSH connection in Linux
Using the SSH key on the remote server, you can now test if your connection is working properly.
Log in with the following command:
ssh username@ip_remote_host
The remote host will log you in without asking for the user account password.
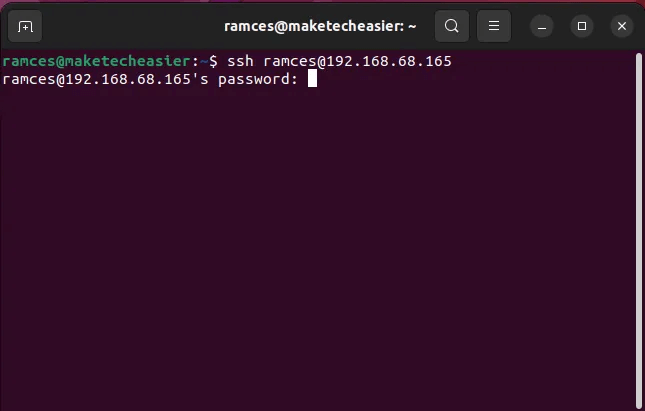
However, if you make a mistake during the process, the SSH daemon will automatically revert to password authentication for your user account. This allows you to continue accessing your remote server even if your RSA key doesn't work.
Configure SSH to block passwords
For optimal security, you should disable SSH password logins on your Linux server. Similar to enabling two-factor authentication in SSH, this prevents anyone from forcing their way into your server.
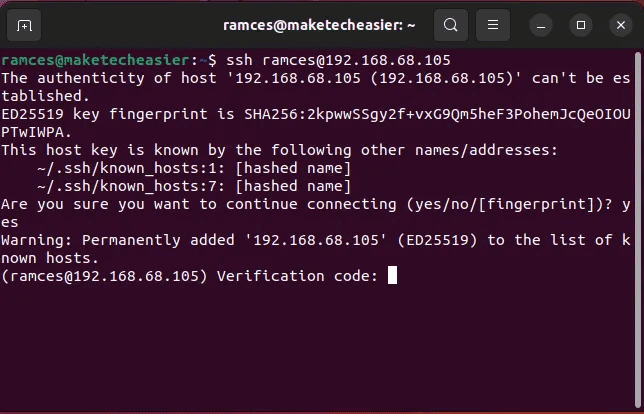
It's important to ensure you can reliably log in with your SSH key before doing this, as it's possible to lock yourself out of the remote server if you have a broken key.
You can find the configuration file. SSH daemon yours in “/etc/ssh /sshd_config”. Open the file on the server using sudo and your favorite text editor. For example, open this file using nano by running the following command:
sudo nano / etc / ssh / sshd_config
Find the lines below by clicking on Ctrl + W Edit it to look like the example. Uncomment both entries and change the values to No.
Password
PasswordAuthentication no PermitEmptyPasswords no
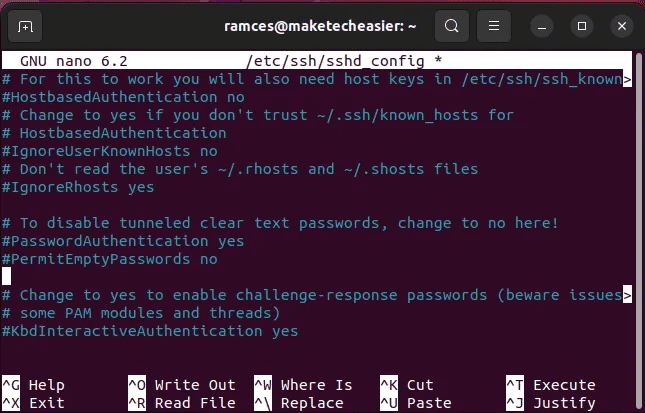
set Password Authentication Whether you want to use password authentication. We set this to "no" Because we want to use only SSH keys.
Determines AllowEmptyPasswords Whether the server allows logins with a blank password. It should never allow this, so we set it to "no".
Next, find the “UsePAM” line and change it to “No.” This will prevent the daemon from using any authentication methods (password, Kerberos, etc.) other than SSH keys.
UsePAM no

Save the file by clicking on Ctrl + O , Then Ctrl + X and reload SSH server.
sudo systemctl restart ssh
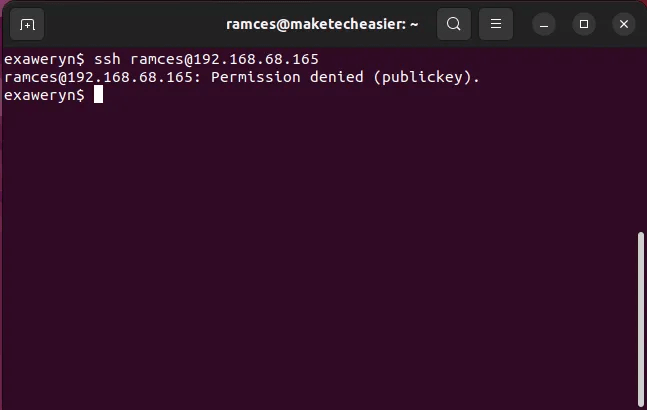
Now that you have successfully configured your server to use only SSH keys for authentication, anyone who attempts to log in without a valid RSA key will be immediately rejected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. I get a "Connection refused" message when I send an SSH key to my Linux server. How can I resolve this issue?
answer. Make sure the SSH server is running on the remote host. You can check this by running sudo systemctl status ssh. If the service isn't running, you can start it with this command: sudo systemctl start ssh.
If a firewall is running on the server, make sure port 22 is open. You can do this by running sudo ufw state. If SSH isn't listed, you can enable it by running this command: sudo ufw allow ssh.
Q2. I get the error “Permission denied (public key)” when I try to log in. What should I do?
answer. This error means that you've configured your server to use keys for authentication, but you're still trying to log in with a password. This could be due to either a missing RSA key or an incorrect SSH setup. Make sure your public key is copied to the server correctly and that you specify the correct public key when connecting.
Q3. I get the error message "Host key verification failed" when I try to connect. How can I resolve this issue?
answer. This error means that the SSH server's host key has changed. This can happen if the server has been reinstalled. You can regenerate a new public key and copy it to the remote host. Repeat the steps in this article to regenerate the new key and add it to the server.
Q4. Is it possible to use multiple SSH keys on the same remote Linux server?
answer. Yes. You can use the -f option in OpenSSH to specify the exact key you want to use to connect to a remote server. For example, running
ssh -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_2 username@remote_ip_address
To connect to your remote server using the “id_rsa_2” key instead of the default “id_rsa”.
However, it's important to note that this command will only work if the remote server already knows your new key. You'll first need to copy it to your remote server using ssh-copy-id. Similar to the steps above, you can do this either through password or RSA key authentication.
Q5. I get a “Permission denied” error when I try to copy the SSH key to my server.
answer. This issue is most likely caused by a permissions issue on your remote server. In most cases, the ssh-copy-id utility should resolve any access issues correctly once it connects to your remote server. However, there are instances where this feature malfunctions and fails to correctly copy the "id_rsa" to your local machine.
To fix this, log in to the remote server and run
chmod 700 /home/$USER/.ssh/* && chmod 600 /home/$USER/.ssh.
This will set the correct permissions bit for both the “.ssh” folder and its contents.