The central processing unit (CPU) (or processor) is the brains of your computer, so it's essential that it runs smoothly and efficiently. Under stress, your CPU's temperature can start to rise, at which point your computer may start to slow down and crash—and in the long run, your CPU may even die. Here's how to cool your CPU—from tracking temperatures, to figuring out how hot it is, to finally fixing the problem.
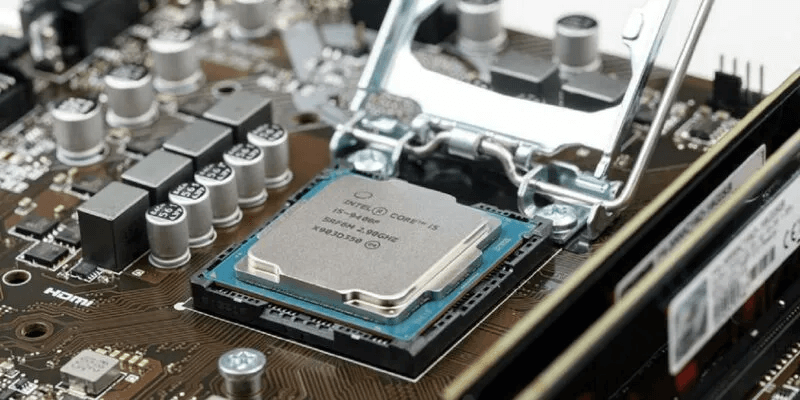
How to monitor your CPU temperature
It's very easy to check your CPU temperature. If you're using Windows, Speccy It's a great diagnostic tool that tells you everything about your computer, including your CPU temperature. MSI Afterburner It is another great tool for monitoring CPU and GPU temperatures.

Mac users can grab Fanny, which doesn't go into as much detail as Speccy, but sits as a widget in the notification center for easy access to CPU and fan statistics. Linux enthusiasts can check their CPU temperature with the tool psensor .
How hot is my CPU?
This is where things get a little complicated. Different processors are built differently; as such, each has its own limits on how far you can push them. A temperature of 80 degrees Celsius, for example, can be ignored by some processors and cause serious damage to others.
When idle
Regardless of the processor model, ideal idle temperatures don't vary much. “Idle” When you turn on your computer but don't open anything, and the operating system isn't doing anything else intensive (such as Windows' Superfetch process), the average idle temperature should be around 30 to 40 degrees Celsius.
When under heavy load
If you're using an Intel CPU, look up your processor's specifications. You're looking for a statistic called TJunction Or TJ Max. This number is the absolute maximum it can handle before problems occur. As a general rule, try to keep your processor temperature 20 to 30 degrees Celsius below this maximum at all times to ensure you don't cross the dangerous line.
For example, it contains Intel Core i5-9500 on TJunction of 100C. If you use this processor, you will need to ensure that it never exceeds the range. 70 To 80°C. AMD A little easier: just find the specifications. Max Temps On the processor product page. Features: Ryzen 5 2600 times بMaximum temperature is 95°C So try to keep it lower than 65 To 75 degrees Centennial to maintain her health.
Identify and reduce high CPU usage
Once you've confirmed that your CPU is indeed overheating, it's time to try to determine the possible cause. Potential problems could lie with either the software or hardware side of your computer, so there's plenty to consider.
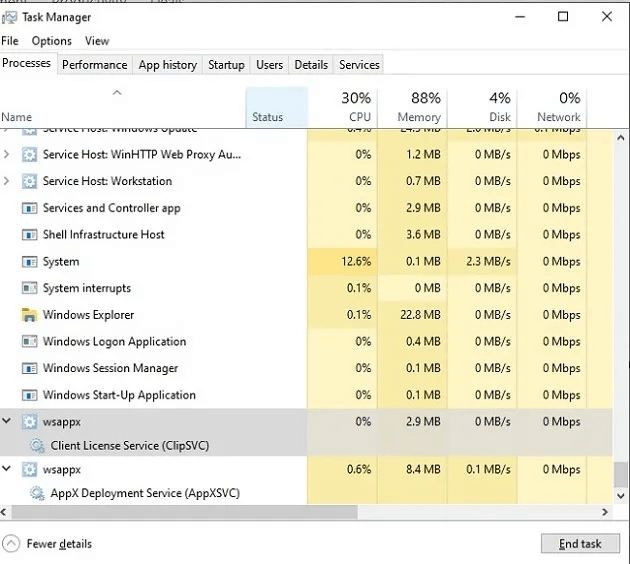
It's easier to start with software solutions, so one of the first things you can do in Windows 10 and Windows 11 is press Ctrl + Shift + Esc and see if you have High usage Abnormal CPU performance. Weaker CPUs are often under heavy pressure from some Windows processes and services, and we've compiled a list of them. Common Fixes for High CPU Usage in Windows 10.
1. Clean the dust.
Cleaning your computer can do wonders for your temperature gauges. If your fan speed seems too high, you may need to open up your computer and clean it.
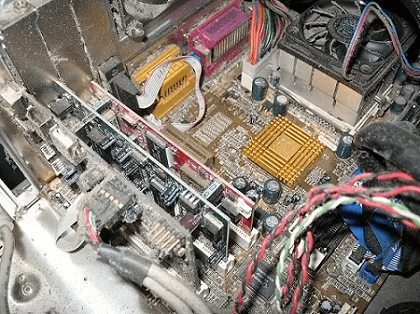
Too much dust can clog fans and heatsink fins, but fortunately, cleaning the inside of your computer is easy. Ground yourself when touching metal to prevent electrical shock to computer parts. Using compressed air from a distance of 6 inches, blow dust clumps off fan blades, the power supply, the motherboard, and all other components. For hard-to-reach areas, use a cotton swab dipped in >90% isopropyl alcohol. Do not restart your computer if moisture remains.
2. Reinstall the cooling chamber.
If you apply thermal paste and your CPU temperature doesn't drop after a few days of short downtime, your heatsink may be improperly seated. When this happens, the heatsink doesn't make full contact with the processor, which can cause it to overheat.
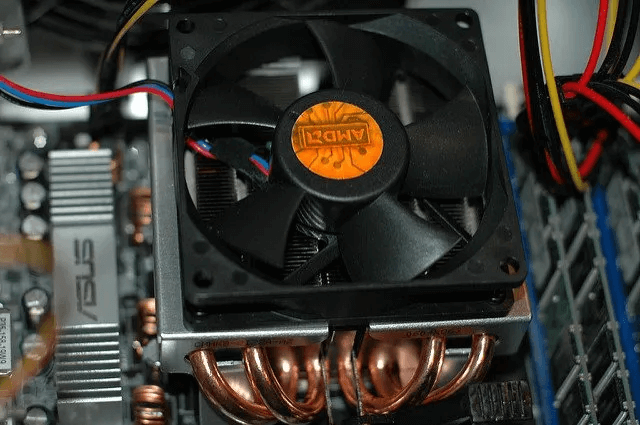
To fix this, simply remove the heatsink and replace it on the processor. Ensure it aligns with the mounting points around the processor's perimeter and secure it in place using a screwdriver or tabs, depending on the heatsink.
3. Invest in a new CPU cooler/heatsink.
A CPU cooler keeps the chip cool by drawing heat away from the CPU toward the motherboard/heatpipes. Heat transfers from gas to liquid through the condenser and is cooled by the fins of the heatsink and fan. This "cooled liquid," or refrigerant, makes its way back through the evaporator so it can be used again.
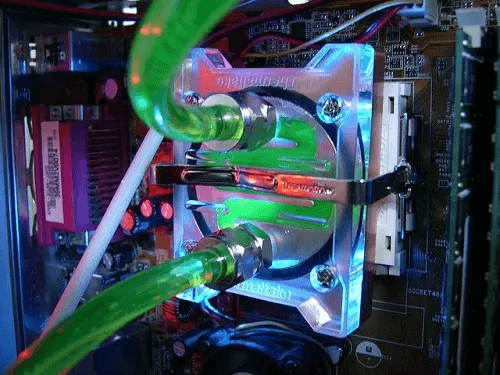
The whole process is to reuse the same heat originally generated by the CPU. If your CPU cooler/heatsink is old, this heat won't be recycled. If you want to look into this further, .
It's also helpful to understand the difference between air cooling and liquid cooling, the two main methods for cooling CPUs. With air cooling, a heatsink with a fan is attached to the CPU using thermal paste. As the fan runs, heat is dissipated. This is the most common setup and is also the reason you'll hear the fan running more loudly as CPU usage increases.
Liquid coolers use small caps to attach to the CPU. Coolant is added through tubes and a radiator to help cool the CPU. A fan is attached to the radiator, as is a heatsink, to dissipate any heat buildup. While you can build your own custom loop liquid cooling system, it's difficult to manufacture—but it performs far better than other solutions.
In general, liquid coolers offer better performance and are quieter. However, air cooling is more affordable and easier to maintain.
4. Reapply thermal paste.
Thermal paste fills the gaps between the CPU's processor and heatsink and helps transfer heat efficiently. Running a CPU without thermal paste is like driving a car without oil. And what happens when you ignore obvious warning signs, like the check engine light? Instant engine failure.
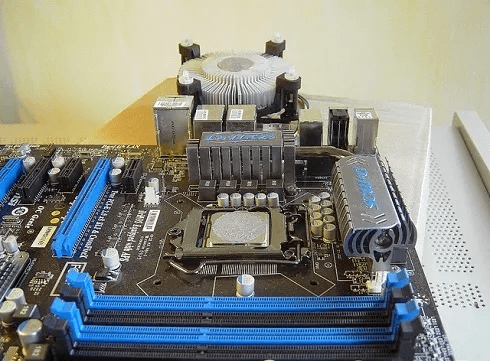
Follow these steps:
- Choose the right thermal paste for your CPU. Ceramic is the easiest and most versatile to work with. Thermal Grizzly Cryonaut و GELID GC-Extreme Two great and affordable options. If you want better CPU performance, choose a liquid metal thermal paste. However, they are difficult to apply, and even a small mistake can damage your computer. Thermal grizzly conductonaut Good choice.
- Turn off your computer and disconnect all cables.
- Gently remove the heatsink from the processor.
- Gently clean the heatsink to remove any remaining paste. You may need to use Q-tip. For anything that doesn't come off easily, you can use more than 90% isopropyl alcohol or a thermal paste cleaner like ArctiClean.
- Apply a pea-sized amount of thermal paste to the center of the processor. Don't apply more than this; it only takes a tiny amount. You can also apply a few thin lines or even spread it evenly using a piece of cardboard or a gloved finger. Just try to avoid getting any paste on any other components.
- Gently replace the heatsink and screw it back on.
- Monitor the temperature over a few days using a specie.
Ideally, you should reapply the paste every few years for optimal performance. If you tend to push your CPU to its limits regularly, such as hardcore gamers, you may want to reapply annually.
5. Check for malware infection
A severe malware infection will cause your CPU to work harder and your computer to run more slowly. Some common malware infections that cause a severe increase in CPU temperature include:
- Viruses (system infectors, file and macro communicators)
- Trojans (backdoor, rootkit, exploit, among many others)
- Worms (email, internet, network)
Malware that uses a lot of resources tends to generate high CPU temperatures and noisy fans; notable examples are Bitcoin Miner viruses (Otorun, Kolab, BTMine). We conducted our annual review of Windows Defender and found it to be as effective as the best third-party antivirus, but if you want a lightweight tool to add an extra layer of security on top of that, Malwarebytes It's a favorite here at MTE.
6. Stop overclocking
Overclocking is when you increase your CPU speed/clock rate through a BIOS setting, increasing your computer's overall performance—but at a small cost: Overclocking = increased CPU heat generation = higher temperatures. But this isn't always the case. If you invest in a good heatsink/CPU cooler setup, your CPU should stay cool at all times.
However, if you overclock excessively with a substandard cooling system, the CPU will overheat, throttle, and potentially cause system failure. We mentioned MSI Afterburner earlier, which is also an overclocking program. Here's an overclocking guide for the tool, which also explains how to disable overclocking.
7. Give your computer some space.

It's not uncommon to tuck your computer tower away from view or to prevent damage. However, computers need room to vent. If it barely fits anywhere, consider moving it. You should have at least a few inches of space on all sides.
If you leave it running in a closed computer case, you're likely to experience more CPU overheating issues. You can still put it in a case, but consider installing a fan to vent the heat or leaving the door open whenever the computer is running.
8. Replacing or adding ventilation fans

If your computer isn't specifically designed for heavy CPU usage and overclocking, the fan may not be equipped to cool as much as you need. Most standard computer fans are designed for average use. Anything higher than that will result in higher CPU temperatures.
Consider replacing your CPU fan with a higher-performance model. It will be much better, helping your CPU's overall performance and health.
Another option, especially if your CPU fan is already the best you can get, is to install a case fan. As the name suggests, this is an additional fan that draws heat away. Or you can opt for a dual-fan approach with an intake and exhaust fan. One draws in cool air, the other pulls out hot air. Just make sure the fans are matched to avoid any pressure issues in your PC. Some options that work well include: Corsair ML120 و Corsair AF140 LED Low Noise Cooling Fan و Cooler Master Sleeve Bearing 80mm Silent Fan.
The last fan to check is the power supply fan. If it isn't working properly and you don't have a case fan, there isn't a fan to extract heat from your computer. If it isn't working properly even after cleaning it, consider replacing it to help dissipate heat from the entire case.
9. Cleaning cables
Adding components to your case is great—but not if it leaves behind a tangled mess of cables. No matter your cooling system, air won't dissipate well if there's a tangle of cables blocking the fan(s). All you need to do is arrange your cables so they're out of the way of the fan(s) and CPU. This can involve using cable ties and adhesive hooks to pull cables out of the way, and even using shorter cables when possible.
10. Use a laptop cooler.

For laptop users, you can't really use some of the options mentioned above, such as adding more fans. However, you can use a laptop cooler. These feature fans that help dissipate heat from your laptop. They also double as a laptop stand. They can work well if you tend to keep your laptop on your lap while gaming or doing other CPU-intensive tasks. You'll need a free USB port to power them.
Some of the most popular options include: Havit HVF2056 Laptop Cooling Pad and ICE COOREL RGB Laptop Cooling Pad وLIANGSTAR Laptop Cooling Pad.
11. Adjust your CPU settings in Windows
Although it's not always an ideal solution, you can adjust your CPU settings in Windows to reduce overheating issues. Lowering the maximum setting helps prevent your CPU from being used at 100 percent. This also reduces high temperatures. The idea is to find a comfortable balance between performance and temperature.
Go to "Start" Or "research" And type "control Board" , then open "control Board".
Choose Hardware and Sound -> Power Options -> Change plan settings -> Change advanced power settings.
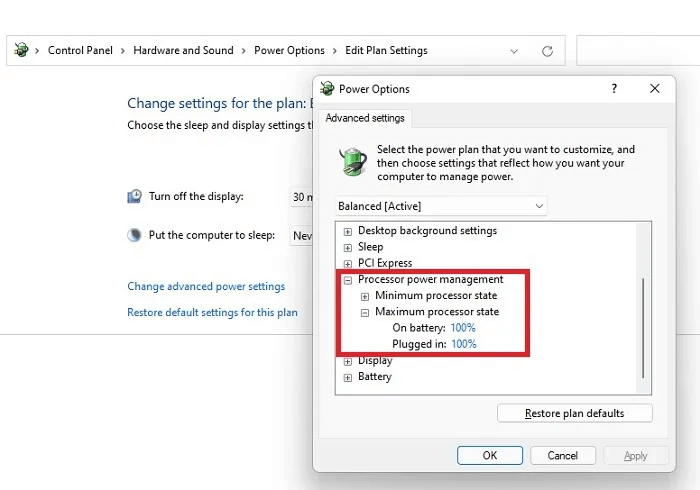
Expand Processor power management و Maximum processor stateChange the percentages to 80 or 90. Then see how your CPU temperature changes after a few days. Try to stay as close to 100 as possible. If you go too low, you'll see a significant drop in performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Will keeping my computer open help me?
answer. No. As strange as it may seem, a sealed case works best. Otherwise, your fans will draw in a lot of dust and debris, which can lead to higher CPU temperatures. Additionally, it's best to keep all your computer components clean.
Q2. Is my CPU dead?
answer. Excessive heat can cause your CPU to fail. However, high CPU temperatures aren't usually a sign that your CPU is dying. Instead, you'll experience startup issues and random crashes.
But when your CPU gets too hot, your computer can also crash. If this happens, your CPU is likely still fine. You just need to focus on the above to reduce your CPU temperatures in the future.
Q3. Should I let my CPU cool down before restarting my computer?
answer. If your computer shuts down and feels hot, let it cool down before restarting it. Otherwise, your CPU temperature will rise again. Write down what you were doing to see if you were demanding too much from your computer. Or check to see if there are other issues, such as dirty fans, non-working fans, insufficient thermal paste, etc.
Q4. Do I need to replace my box?
answer. If you have an older case that doesn't provide much ventilation, you may want to consider upgrading to a newer one. Some already have built-in fans, and they may also have vents on the sides in addition to just the back. You'll need to use compressed air to clean them more often, but they tend to cool the case better.
Finally
Hopefully, your computer is in good shape now, but it can also be affected by rogue Windows updates. Check out our guide to learn how. Latest Windows 10 Issues And how to fix it. Another vital health check is your hard drive, and we've covered that. Monitor SSD or HDD status Also.