Having a fast Wi-Fi network has become essential in our daily lives. From browsing the internet and working from home to playing online games and streaming Netflix, we rely on a strong Wi-Fi connection. But not all Wi-Fi networks are created equal. With so many Wi-Fi technologies available, which should you choose? Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E: What are the differences? And, more importantly, should you care?

Tip: You can Installing custom firmware on your router and access to additional features.
What are the current Wi-Fi standards?
Every few years, we witness a leap in Wi-Fi technology. To understand and compare different Wi-Fi technologies in a practical way, we need to look at the set of standards that routers, routers, and other networking devices adhere to. These standards are developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and are overseen by the Wi-Fi Alliance.

Before Wi-Fi 6, the latest Wi-Fi standard, the naming convention was more confusing. We used to notice different Wi-Fi technologies using “802.11xx.” Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 4 are now retroactively named 802.11ac and 802.11n, respectively. Meanwhile, Wi-Fi 6 is also known as 802.11ax. The new naming convention is more helpful and easier for the average person to understand.
Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 are currently the most readily available standards supported by the majority of devices. The newer Wi-Fi 6E brings some upgrades over Wi-Fi 6, but it's not yet widespread. But what's the difference between existing Wi-Fi standards?
Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6
The Wi-Fi 5 standard was released in 2014 and remained the most widely used Wi-Fi standard worldwide for several years. With the release of Wi-Fi 6 in 2019, Wi-Fi 5 quickly became obsolete. Wi-Fi 6 brings some significant improvements over its predecessor.
The first—and perhaps most important—improvement is speed. Wi-Fi 6 boasts a theoretical data transfer speed of 10 Gbps, compared to Wi-Fi 5, which only reached 3.5 Gbps. While actual real-world performance will be determined by home device setup and physical obstacles, Wi-Fi 6 brings a significant speed upgrade over Wi-Fi 5.

The second major improvement is latency. Wi-Fi 6 reduces the latency of wireless networks, resulting in improved download times and fewer dropped connections. Using technologies like orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA), Wi-Fi 6 is more efficient at transmitting data packets over a wireless signal.
The next upgrade concerns network congestion. With multiple devices competing for the same bandwidth, Wi-Fi 5 networks can't keep up. MU-MIMO allows Wi-Fi networks to stream data to multiple devices simultaneously in both directions. Since Wi-Fi 5 only supports up to four streams, it doesn't play well with Wi-Fi 6, which can support up to eight streams.
Wi-Fi 6 is not only faster than older Wi-Fi standards, but it's also more reliable. Note that Wi-Fi signals use the best channel within the frequency range to transmit data. Wi-Fi 5 needs to wait for a clear channel before transmitting a signal. On the other hand, Wi-Fi 6 is better able to identify the source of interference that is blocking a particular channel. This enables it to continue transmitting in cases where other networks are interfering with your own network.
Wi-Fi 6 also shines in the area of battery efficiency. On supported devices, Wi-Fi 6 can customize how Wi-Fi signals are received. It helps devices temporarily turn off reception when the device is inactive, helping to conserve battery life.
Finally, Wi-Fi 6 is more secure than Wi-Fi 5. With support for the WPA3 standard, network encryption on Wi-Fi 6 is more difficult to crack than on older Wi-Fi standards.
Good to know: Do you just need to get a new router? Learn the difference between Access Point and Repeater modes..
Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E
The Wi-Fi 6E standard was introduced in 2020, with devices supporting the new technology becoming available a few months later. "TO" On Wi-Fi 6E to “Extended”. This is because the new standard expands the capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 into the new 6 GHz frequency range.
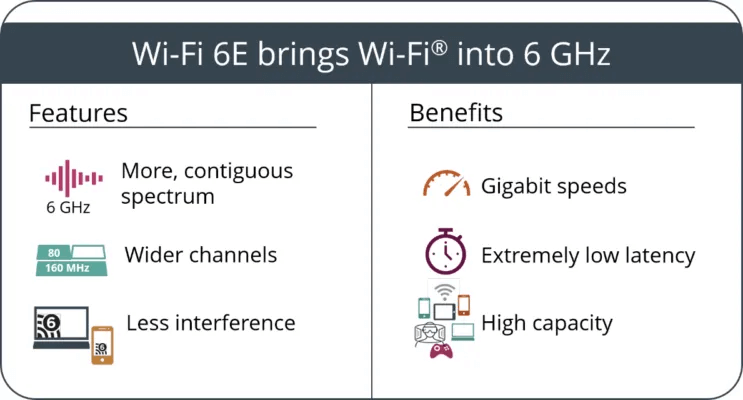
Wi-Fi 6E has access to more and wider channels with much less signal congestion than the already feature-rich Wi-Fi 6 networks. Consequently, Wi-Fi 6E experiences less interference from other bands and older devices and lower latency compared to Wi-Fi 6. It's not perfect, though, as it becomes less reliable over long distances and through thick walls. This is because 6 GHz radio waves are less adept at dealing with obstacles than lower frequencies.
Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E
You may still be using some devices that support Wi-Fi 5, but they are quickly becoming rare. Wi-Fi 6 devices and routers have gained rapid popularity as router costs have dropped. At the same time, device manufacturers have adopted the newer standard for many of their products.

However, Wi-Fi 6E support has remained patchy at best. Routers that support Wi-Fi 6E remain expensive, and device support remains limited to high-end phones, laptops, and TVs.
Currently, the best option based on availability, features, and price is Wi-Fi 6. It supports data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and has almost all the features of Wi-Fi 6E. Regardless of which standard your laptop or PC supports, it will still work with any modern router you have, as both Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 6 routers are backward compatible with devices that support Wi-Fi 5 and older standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What do I need before upgrading to a better Wi-Fi network?
The answer: Before you can enjoy faster, more consistent Wi-Fi, you need to make sure you have all the pieces in place. This includes purchasing a new router and client device (phone, laptop, TV) that supports the Wi-Fi standard you want to use. Also, make sure your actual internet plan can deliver the speeds you want. There's no point in investing in expensive Wi-Fi 6E devices if you can't take full advantage of the potential peak transfer speeds.
Q2: Should I wait for Wi-Fi 7?
The answer: Wi-Fi 7 is the upcoming Wi-Fi standard, promising speeds of up to 40 Gbps. While devices and routers supporting this latest standard will begin appearing in early 2023, don't hold your breath for this one. Even Wi-Fi 6E routers aren't what you would call "affordable," so it will be a long time before we see Wi-Fi 7 devices reach the masses. Furthermore, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E speeds, supported by suitable ISP plans, are currently more than sufficient for most use cases.
Q3: Does Wi-Fi 6 penetrate walls better than Wi-Fi 5?
The answer: All other things being equal, yes, because Wi-Fi 5 only operates on the 5 GHz band, while Wi-Fi 6 is capable of operating on both the 5 GHz band and the 2.4 GHz band. This allows Wi-Fi 6 signals to have a longer range and better wall penetration than Wi-Fi 5's 5 GHz signals. Some users even route and combine the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands to achieve optimal Wi-Fi performance.
Q4: Is it worth buying a Wi-Fi 6 router if I have a Wi-Fi 5 device?
The answer: If you have an older phone or laptop that only supports Wi-Fi 5 speeds, you may still consider investing in a Wi-Fi 6 router to take advantage of the other benefits. You can improve connection latency and congestion, and achieve a generally reliable Wi-Fi network—though you'll be limited to Wi-Fi 5 speeds.








