A stable and reliable Ethernet connection is essential to unlocking the full potential of fiber optic broadband, especially for office users. However, users often find their Ethernet speeds capped at 100 Mbps, even on a Gigabit Ethernet network. This guide attempts to fix the 100 Mbps Ethernet speed limit on Windows and resolve this strange but common error that affects many Windows users.

Tip: Do you Your Ethernet connection is not working.Try these fixes.
1. Ensure proper cable connections.
When connecting Ethernet cables to your computer or router, you should hear an audible click or snap once the cable is securely in place. Sometimes, the Ethernet cable isn't fully connected, or the "clip/tab" on the cable connector (RJ45 connector) becomes loose or breaks completely. This can cause the connection between the connector and your computer/router to become less stable.
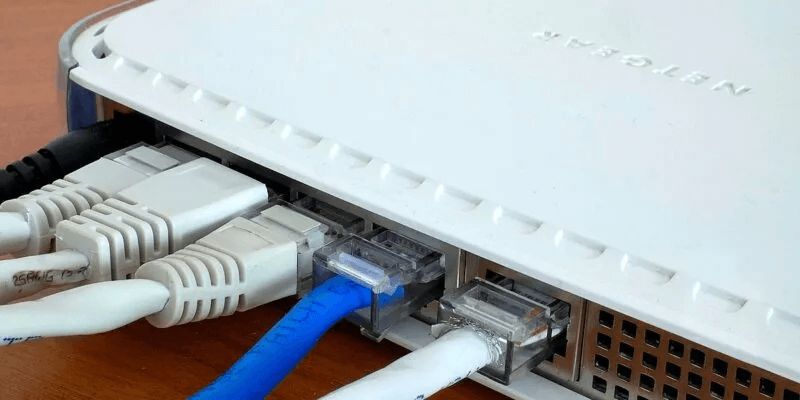
A loose cable can cause a drop in speed on a high-speed connection of 200 Mbps/300 Mbps or faster as the default network will be 100 Mbps.
To fix this, unplug the Ethernet cable from both the router and the computer and reconnect it after about 30 seconds. Make sure the cable is securely connected at both ends. Even with a broken clip, you can push the cable all the way into the LAN port to eliminate the loose connection as the source of the limited speed.
2. Check the Ethernet cable.
If all Ethernet connections appear to be in good condition, the problem may lie with the cable itself. Ethernet cables are rated according to their data transmission capabilities. Common Ethernet cables used in home and office networks are Cat5, Cat5e, and Cat6. Less commonly used cables are Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8.
If your home network uses a Cat5 Ethernet cable, your speeds will be limited to a maximum of 100 Mbps, as this is the data transfer limit for Cat5 cables. Therefore, you may simply need to replace your cable with at least a Cat5e cable, which can transfer data up to 1000 Mbps.
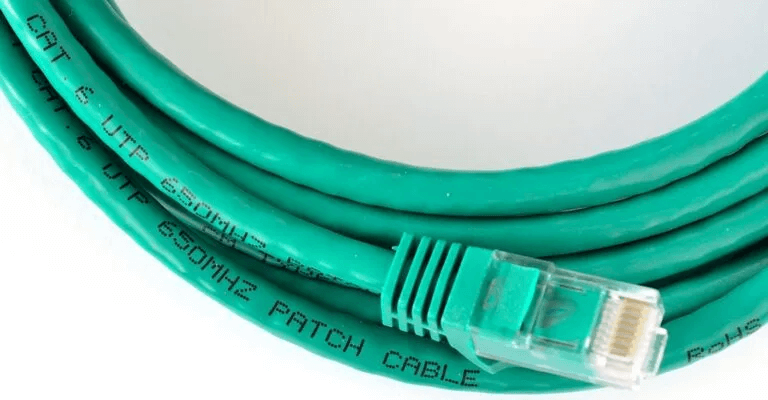
To determine the type of Ethernet cable you currently have, look at the cable jacket. You'll be able to find text on the jacket that will indicate whether the cable is Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, or something else. If there's no text on the cable jacket, it's difficult to determine the cable type, as there are only slight differences in thickness and internal wiring between different types of cables. For more details, check out Things to Know When Buying Ethernet Cables.
3. Replacing RJ45 connectors
Switching from a lower-bandwidth cable like Cat5 to a higher-bandwidth cable like Cat5e or Cat6 should ideally resolve the issue with limited Ethernet speeds. However, if you're still experiencing intermittent speed drops on your Gigabit connection, the RJ45 connectors at the ends of your Ethernet cable are likely the culprit.
Often, home setups involve routing Ethernet cables internally within walls. This creates a cleaner appearance and protects the cable from damage. Often, the default RJ45 connectors pre-applied to the cable ends are too large and need to be removed before routing the cable through walls. This inevitably requires re-crimping, or reattaching, the new connectors to the cable ends once they exit the other end.
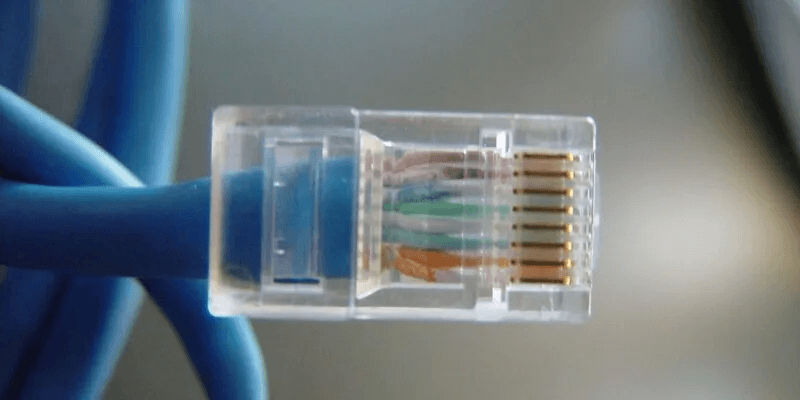
At this point, issues will creep in. Either the new RJ45 connector you're using isn't compatible with the cable's internal wiring, or the re-crimping process is faulty. If one of the internal wires isn't properly connected to the metal contacts of the connector, your connection speed will drop to 100 Mbps.
Therefore, consider replacing the RJ45 connectors with high-quality, shielded ones. This is recommended only after replacing the cable itself and the problem persists.
Good to know: These methods may help you: Fixing a slow Wi-Fi connection in your home.
4. Check your Ethernet adapter settings.
If you've eliminated the physical sources behind the error, it's time to move on to the software side of things. Your computer's Ethernet adapter settings are likely limiting your connection speed to 100 Mbps. There are several settings here that you need to check. To ensure your adapter settings are configured correctly, follow the steps below:
- Search for an app Settings And open it from Windows search.
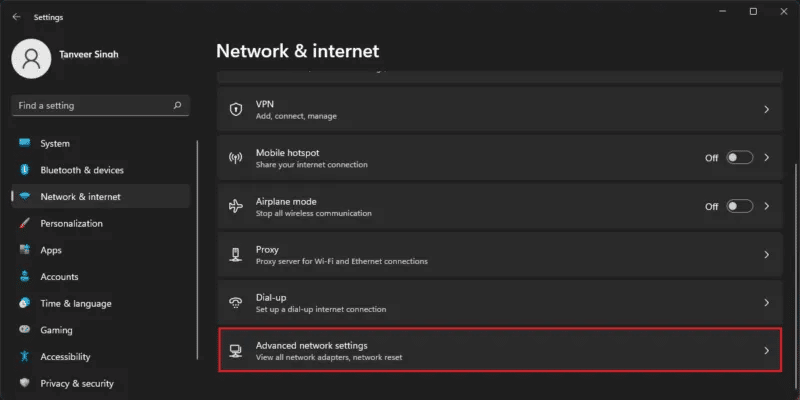
- Locate “Network and the Internet” From the options on the left, then Advanced Network Settings in the right pane.
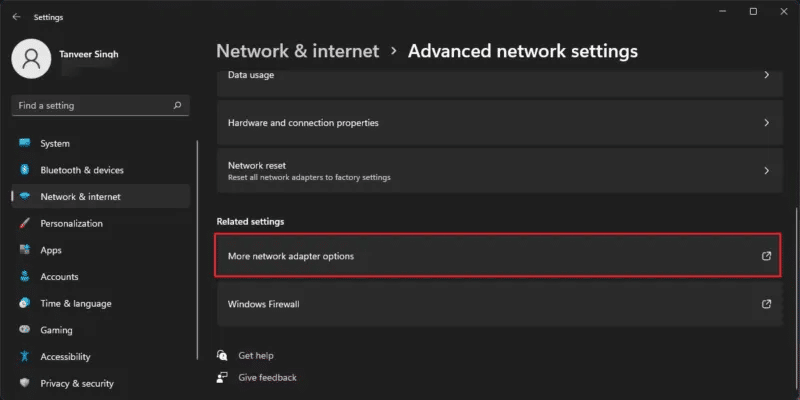
- tap on More network adapter options within Related Settings.
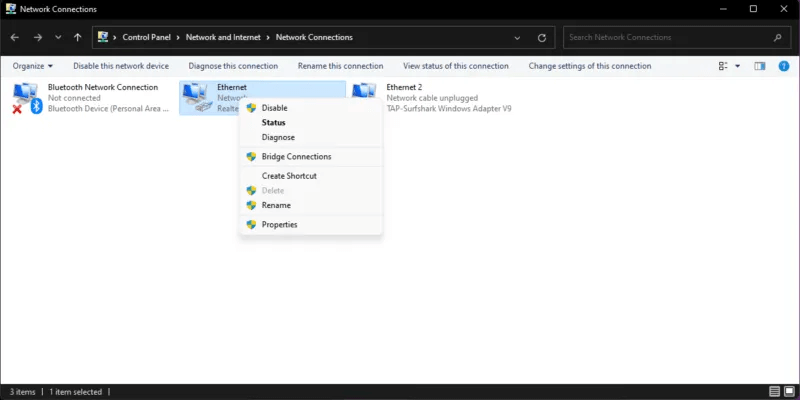
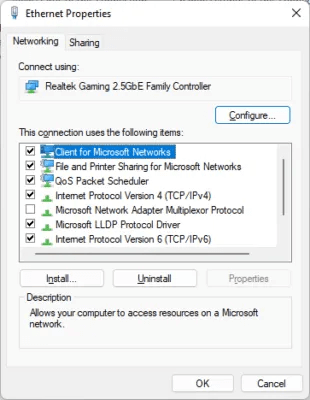
- In the new window titled Network communications Right-click on the Ethernet adapter and click "Properties". Windows 10 users can click on “Change adapter options” After step 2 to open a window Network communications.
- In the new Properties window, click the button "formation" To unlock additional features.
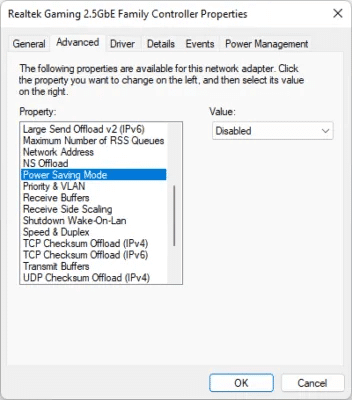
- Open the tab "Advanced Options" At the top, select Speed and duplication from square "The property".
- Make sure its value is set to the right. "Automatic negotiation"This setting will ensure that your computer negotiates the fastest possible speed based on your broadband plan and Ethernet cable. Note that you should not choose any other value, such as 1.0 Gbps Full Duplex , because "Automatic negotiation" This is the recommended setting.
- Go to other settings that may be limiting your Ethernet speed. Make sure the following settings are set to: "Disabled": Energy-efficient Ethernet و Gigabit Lite و Green Ethernet و Power saving mode.
- Click "OK" Allow the adapter a few seconds to reconfigure the new settings. It will disable itself and reconnect to the Internet after a few seconds.
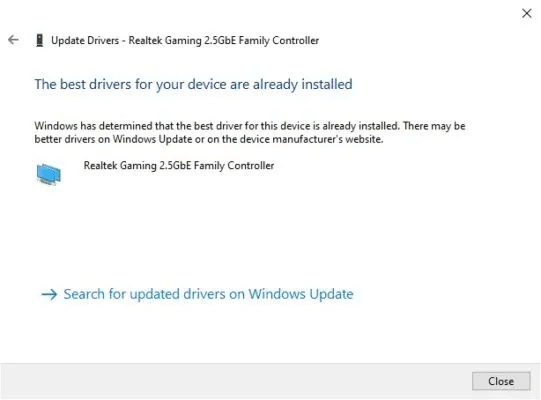
5. Update Ethernet drivers
Configuring the settings in the previous section correctly should resolve the slow speed issue for most users. However, if you still can't fix it, you can try updating your Ethernet adapter drivers. Outdated drivers often cause a variety of issues, one of which can be a limit on Ethernet speed.
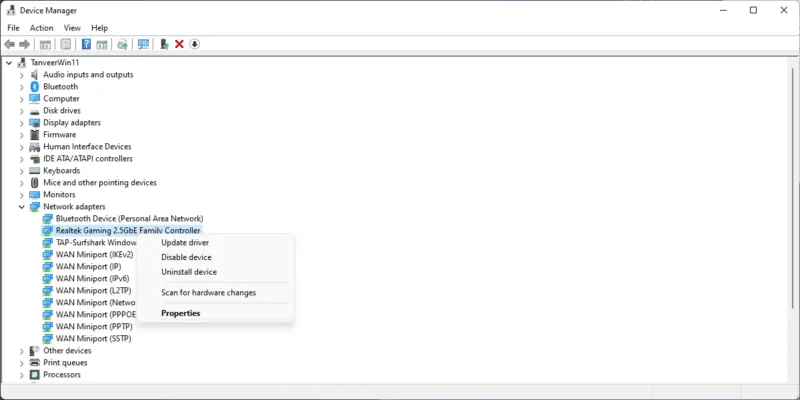
- Right-click the Windows icon and select "Device Manager".
- within Network adapters Right-click on the Ethernet adapter name and click "Update Driver"The network adapter will likely have a name. Realtek Or Broadcom Or Intel.
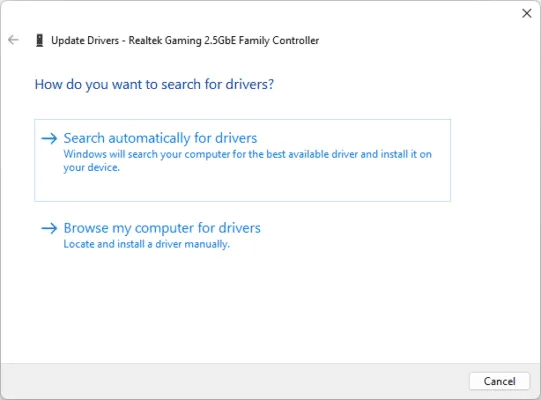
- Locate “Search automatically for drivers” Let Windows search for the latest network drivers for your adapter.
- If available, new drivers will be installed automatically. If not, you'll see the message: “The best drivers for your device are already installed.”
Tip: Open more settings by Installing custom firmware on your router.
6. Check your router settings.
Some routers have settings configured in a way that resets the connection to the default mode. "light or green" , where the network speed is capped at 100 Mbps. This may be one of the reasons for the low speed issue for many users. You can log into your router's settings and reconfigure the settings to solve the problem by following the steps below:
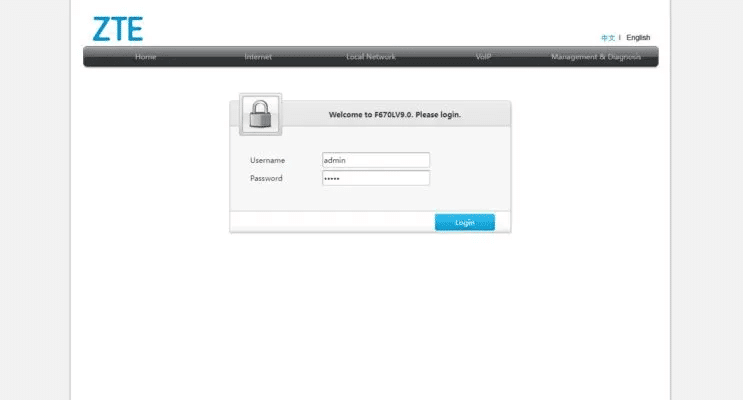
- Enter "192.168.1.1" In a browser window, open the router login page. This IP address is a common factory address for consumer routers. Enter "Admin" In my field "user name" و "password" and click “Sign in”. If that doesn't work, check your router. You should find the username/password information on the back.
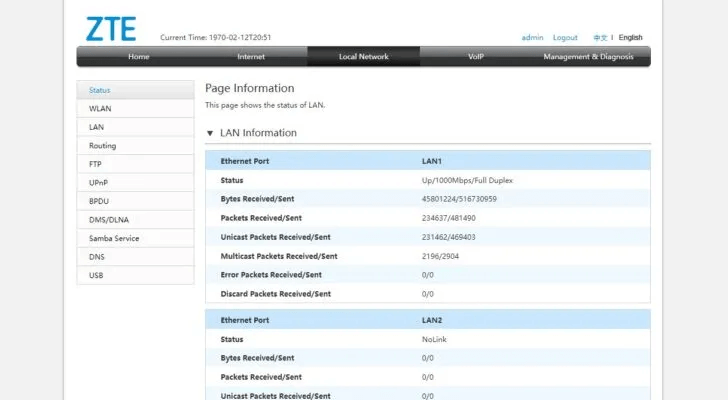
- Find the settings related to your Ethernet connection. They will likely be found in menus labeled something like: local area network Or LAN Or “Ethernet”. Go to that page and find the setting that contains "double" In the name. Make sure it is set to "automatic" Or 1 gigabit per second Or 2.5 gigabit per secondYou will see these options depending on your network adapter.
- It's also possible that you can't find any way to manually change your network speed in your router's settings. In such cases, you can look into other fixes.
Good to know: Learn the difference between “Access Point” and “Repeater"On your router.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Cat5e cable enough for Gigabit LAN?
answer. Cat5e Ethernet cables are technically capable of Gigabit speeds, but they are inferior to Cat6 cables in terms of grounding and overall cable durability. This is a common source of failure in Cat5e cables, which can lead to unstable connections and slower speeds, even though they are technically certified for speeds up to 1 Gbps. It's best to choose a high-quality Cat6 cable to reduce the chances of connection problems caused by the cable.
Q2: Can 2.4GHz Wi-Fi support 100Mbps?
answer. The 2.4 GHz band can technically support speeds up to 1.2 Gbps on routers. Wi-Fi 6 When paired with a sufficiently fast internet plan, this should be enough. However, in practical situations, most people using the 2.4 GHz band likely have Wi-Fi 4 or 802.11n routers, as Wi-Fi 5 only supports the faster 5 GHz band. In these cases, the theoretical maximum for the 2.4 GHz band is around 300 Mbps. However, with other factors such as interference from other devices and congestion from other networks on the 2.4 GHz band, actual speeds drop even further. Generally, you can expect less than half of your plan's rated speed on the 2.4 GHz band. Try band steering to get the most out of both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Q3: Does the length of the Ethernet cable affect the speed?
answer. Yes, Ethernet cables have a rated distance limit beyond which transmission speeds tend to decrease significantly. For example, Cat7 cables can transmit up to 100 Gbps, as long as the cable is within 15 meters or 50 feet in length. The distance limits for Cat6 or Cat5 are more relaxed, and they can maintain most of their speed up to about 100 meters or 300 feet. In practice, cable lengths as long as 300 feet are rarely found in home installations. Therefore, the reduction in speed due to distance is not a significant issue.
Q4: How do I know if my router is Gigabit?
answer. To support internet speeds above 100 Mbps, you need a Gigabit router. Typically, your ISP or Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides a compatible Gigabit router for high-speed fiber broadband plans. However, if you already own an older model and route your internet through it, you may want to check if your router supports Gigabit. You can check the router model printed on the front or back, and then check its specifications online.