If you're looking to build or buy a powerful gaming rig, you'll want to pay close attention to your graphics card. Buying a GPU can be tricky, as there are so many things to consider, from the type of monitor to the size of your case. It doesn't have to be that difficult, however. Knowing your budget, computer requirements, and performance goals will help you find the perfect graphics card for your needs. Our graphics card buying guide will help you figure out what to look for when purchasing a GPU.

Good to know: After selecting the correct graphics card, read this Other considerations for building a gaming PC.
Where's the Value: NVIDIA vs. AMD
Today, the GPU market is saturated with dozens of viable graphics card options from various AIB (Add-in-Board) companies, but only three companies manufacture the GPU chips that power these cards: NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. While Intel has managed to launch some offerings in the low- and mid-range segments, it still has a long way to go before it can become a serious competitor to Team Green and Team Red. The choice now comes down to NVIDIA versus AMD.
Despite some improvements, AMD's ray tracing and scaling technology still lags behind NVIDIA's. For gamers willing to trade the enhanced visuals of ray tracing for more performance, AMD is the better choice, as it offers better value at today's retail prices, precisely in terms of pixel performance.

AMD cards also offer significantly more VRAM than NVIDIA cards. Modern games are increasingly dependent on VRAM AMD cards are likely to perform better in the long run when compared to Team Green cards.
Performance on different budgets
In the wake of the cryptocurrency boom and a global silicon shortage, graphics card manufacturers have introduced sharp price increases as consumer demand has broken all records. The traditional definitions of "budget" and "mid-range" no longer apply in the current market and are unlikely to ever return.
However, you can still get decent gaming performance if you lower your expectations and are willing to stretch your budget a little. This GPU performance guide ranks current-generation and previous-generation graphics cards based on price and performance.
| GPU | slice | the performance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA GTX 1650, AMD RX 570, AMD RX 580, AMD R9 380, AMD RX 5500 XT, NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti | Beginner | Best suited for light gaming, lenient eSports titles, and many great indie games. Ideal for casual gaming. | |
| NVIDIA GTX 1660 Super, AMD RX 5600 XT, AMD RX 6600, NVIDIA 1650 Super, NVIDIA RTX 3050, NVIDIA RTX 2060 | budget | More demanding games will run at medium to high settings. Ideal for 1080p resolution. | |
| NVIDIA RTX 3060, NVIDIA RTX 3060 Ti, AMD RX 5700 XT, AMD RX 6700 XT, NVIDIA RTX 2070 | medium-term | You'll be able to play the latest games on medium to high settings at up to 1440p resolution. It'll certainly do the job for now, but you may need to upgrade in a year or two. | |
| NVIDIA RTX 4070 Ti, AMD RX 7900 XT, NVIDIA RTX 3070, NVIDIA RTX 3070 Ti, AMD RX 6800, AMD RX 6800 XT, AMD RX 6900 XT, AMD RX 6950 XT | high end | Powerful GPUs are designed for gaming at 1440p Ultra or medium resolutions at 4K, even in the near future. | |
| NVIDIA RTX 4090, NVIDIA RTX 4080, Nvidia RTX 3090, Nvidia RTX 3080AMD RX 7900 XTX | Expensive |
Excessive for most gamers. Primarily for enthusiasts who want to be at the forefront of gaming graphics technology and enjoy high frame rates. |
recommendation
Tip: If you are having trouble with your graphics card, you can Update AMD graphics drivers in Windows.
What to look for when buying a graphics card
Choosing the best graphics card based on your budget is only half the story. You also need to consider other factors, such as compatibility with your PC, GPU VRAM, potential bottlenecks, and TDP. These factors can help you make a better purchasing decision and help you get the most out of your investment. They are also crucial to any potential upgrade decisions you may make to take full advantage of the new graphics card's performance.
1. Compatibility
Nothing can be more frustrating than unboxing your shiny new graphics card only to realize it's too big for your computer case. Before you drop the big bucks, do your homework and find out how much physical space your case can provide. Compare your case's GPU clearance value against the dimensions of the graphics card you plan to purchase. If your case isn't compatible with your graphics card, consider purchasing a new computer case.
Also, take note of your power supply. How many amps can it deliver on 12-volt lines? How many watts is it rated for, and how many XNUMX-pin and XNUMX-pin PCIe slots are there? Review this information with the graphics card you're considering purchasing. If your computer isn't equipped to handle the new graphics card, you'll need to look for a graphics card that requires less power or consider upgrading the power supply.

Finally, check the ports. Some monitors use DisplayPort, others have HDMI, and some older units only use DVI. Make sure the card you're considering has at least one compatible connector for your monitor. It's rare to buy a card with different ports than your monitor. However, if this happens, you may need to purchase an adapter at an additional cost.
2. Bottlenecks
Your system determines the type of graphics card you should purchase. Knowing your system's limitations can save you money and headaches. For example, if you're using an older quad- or dual-core processor, a high-end graphics card will likely be limited, forcing you to sacrifice performance. In this case, you can opt for a mid-range card to prolong the life of your CPU or consider a CPU upgrade If your budget allows.
The display is also a key factor to consider. As 1440p (2560 x 1440) displays become increasingly common, your graphics card must be able to handle the increased pixel count for smoother gaming performance. Similarly, if you plan to run multiple monitors or an ultrawide monitor, you'll need to account for the extra pixels and choose a graphics card that supports them.
3. Memory and bandwidth
While more VRAM on your graphics card doesn't guarantee better performance, it's quickly becoming a deciding factor as games become more demanding, especially at higher resolutions like 4K. Many modern high-end graphics cards come with questionable amounts of GPU VRAM, such as the RTX 3070 Ti, which only ships with 8GB of VRAM. While the card is still more powerful, its longevity is hampered by its relatively small VRAM buffer.
Memory bandwidth is just as important as the memory on your graphics card. Data ready for processing by the GPU is typically stored on the card's dedicated memory, which can be GDDR3, GDDR5 (more recently), GDDR6, or GDDR6X. Note that GDDR6 memory offers twice the bandwidth of GDDR5 clocked at the same speed.

Most modern graphics cards come with GDDR6 memory, and some even come with faster GDDR6X memory. Since memory bandwidth is critical to performance, you should always choose faster memory for better performance.
4. CUDA Cores (NVIDIA) or Streaming Processors (AMD)
CUDA cores, or stream processors, can be your rough guide to comparing gaming performance across GPUs in the same family. CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing language proprietary to NVIDIA that leverages the graphics processing unit (GPU) in specific ways to perform tasks more accurately. A CUDA core is NVIDIA's equivalent of an AMD stream processor.
Be careful when comparing CUDA cores or stream processors across different GPU generations, as architectural improvements generally overcome any fundamental CUDA shortcomings at comparable performance levels. For example, the latest RTX 4080 has 9728 CUDA cores versus 10496 CUDA cores on the previous generation RTX 3090. However, the RTX 4080 is about 20 percent faster than NVIDIA's premium offerings from the previous generation.
5. TDP value
Like the CPU, the GPU generates heat when running demanding games and other productivity workloads. A graphics card's TDP indicates its power consumption under theoretical maximum load. The higher the TDP, the more heat it produces. Therefore, you should always choose a GPU that is the most power-efficient—that is, one that delivers the best FPS per watt.
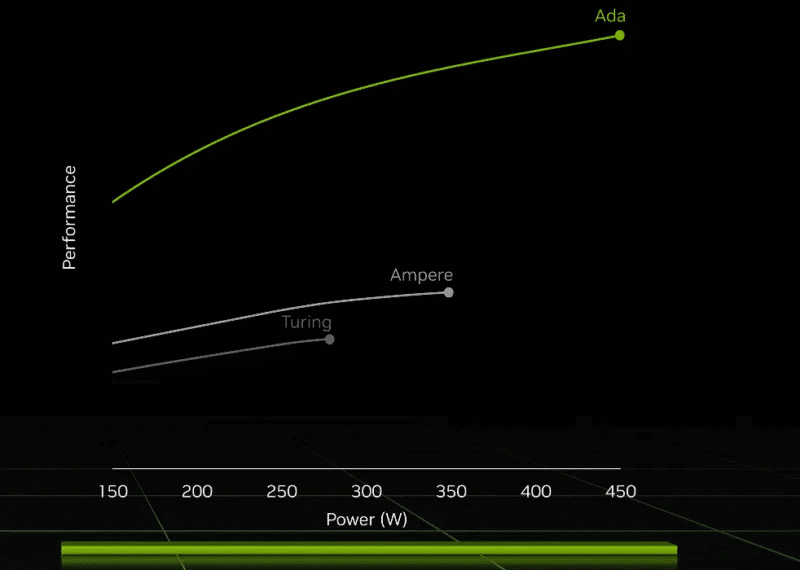
The power consumption of the latest RTX 4000 series has seen a significant jump over previous-generation cards, with the flagship RTX 4090 requiring at least an 850W power supply. AMD's RX 7900 XTX requires at least an 800W power supply to adequately support mainstream GPU performance.
6. G-SYNC or FreeSync?
G-SYNC and FreeSync are adaptive sync technologies developed by NVIDIA and AMD, respectively. Purchasing a monitor that supports one of these features will help adjust your screen's refresh rate based on the FPS generated by the graphics card, reducing issues like screen tearing and input latency.
FreeSync is an open-source standard available on far more monitors than NVIDIA's G-SYNC technology. You don't always need to spend more on a monitor with hardware-enabled G-SYNC technology. Instead, you can choose monitors certified as "G-SYNC Compatible" or get a FreeSync monitor. Purchasing a FreeSync or FreeSync Premium monitor will help you cut costs without sacrificing performance, as both NVIDIA and AMD cards can support FreeSync, similar to FSR available on both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs.
Good to know: If you're using an NVIDIA card, you'll need to know how NVIDIA's GeForce software suite works.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What type of GPU do I need for video editing?
The answer: While video editing is a demanding workload that will benefit from more powerful GPUs, such as NVIDIA's 80- or 90-series cards or similar AMD offerings, purchasing a mid-range GPU will be sufficient for most users. Even when editing 4K videos, a card like the RTX 3060 Ti can significantly increase your workload. The performance gain you'll gain by moving up to a card like the RTX 3090 or RTX 4080 won't justify the associated price increase. It's worth noting that NVIDIA GPUs traditionally offer better support for video editing, XNUMXD modeling, and rendering software than AMD cards.
Q2: Which is better for live streaming: NVIDIA or AMD?
The answer: NVIDIA cards have long outperformed AMD cards for streaming, thanks to their superior NVENC encoder and a host of features targeted at streaming devices. But AMD has now largely closed the gap with its updated AMF encoder and AMD noise suppression, rivaling NVENC and NVIDIA's RTX Voice. AMD graphics cards can now stream video at the same quality and bitrate as NVIDIA cards. The only thing that's needed is industry adoption of AMD's technology; the gap between GPU manufacturers for streaming will become minimal.
Q3: Are NVIDIA drivers more stable than AMD drivers?
The answer: This was the case up until AMD's RX 5000 series. However, when comparing RX 6000 and RX 7000 series drivers with NVIDIA drivers, both brands have experienced driver issues, and it's impossible to declare one better than the other. AMD and NVIDIA do an excellent job of addressing driver issues. While they're not perfect, they do have similar issues that sometimes lead to serious game-breaking errors and system crashes.