Wi-Fi has become the preferred choice for connecting to the internet over wired internet connections for many users. Thanks to its ease of use, Wi-Fi is used across all types of devices, such as laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, and even home automation systems. With the increasing demand for connectivity, it's important to have a reliable and efficient Wi-Fi router that can handle multiple devices and high-bandwidth activities like streaming and gaming. However, with so many options available on the market, it can be difficult to choose the right Wi-Fi router that meets your needs. If you're also wondering how to choose the right Wi-Fi router, you'll want to hear what we have to say.

In this post, we'll walk you through the essential factors when considering a Wi-Fi router. We'll cover important factors like maximum speed, coverage area, Wi-Fi bands, and much more. Ultimately, you should be able to choose the right Wi-Fi router for you.
But first, you might want to check the following:
- Learn the difference between a router and a modem.
- Never go offline when you use these power banks for your Wi-Fi router.
- Save money while playing online with Budget Wi-Fi Gaming Routers
1. Check with your Internet Service Provider
In an ideal world, you could just buy any router and use it with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). But that's not the case. In fact, if your internet connection requires you to use a cable modem with DSL, a random router may not work.
Fortunately, most ISPs have a list of recommended or compatible routers. You can find them on their support pages. Alternatively, if you have two routers on the shortlist, you can simply contact your ISP's customer service to check whether your router is compatible.
2. WI-FI Standards (WI-FI 5 vs. WI-FI 6)
Most routers feature Wi-Fi 5 or Wi-Fi 6 engraved on their packaging. These are Wi-Fi standards defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Each standard supports different bandwidths and speeds. As for the naming convention, each protocol is distinguished by the IEEE 802.11 designation, followed by a set of letters, such as a/b/g/n.

To simplify matters, each criterion is given a separate name. You can check the list below to better understand each criterion:
- 802.11b is called Wi-Fi 1.
- 802.11a is called Wi-Fi 2.
- 802.11g is called Wi-Fi 3.
- 802.11n is called Wi-Fi 4.
- 802.11ac is called Wi-Fi 5.
- 802.11ax is called Wi-Fi 6.
- 802.11be is called Wi-Fi 7.
Each Wi-Fi standard varies in frequency range, maximum data transfer rate, and range. However, at the time of writing, you'll only find two types of routers on the market: Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6. Although Wi-Fi 7 is the latest version, it's still in its infancy, and routers that take advantage of the latest standard aren't readily available.
When comparing Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6, the newer version, Wi-Fi 6, is superior. Wi-Fi 6 can theoretically deliver peak speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps, while Wi-Fi 5 can reach speeds of up to 3.5 Gbps. It can also support more devices simultaneously, is more efficient, and offers slightly better overall range.
Ideally, if your budget allows, it's always a good idea to choose the latest router that supports the latest standard. However, you also need to ensure that the devices you want to connect to your router also support the latest standard. If they don't, there's no point in paying the extra premium. Instead, you can save money and opt for cheaper Wi-Fi 5 routers.
3. Maximum speed
One of the first things to consider when choosing the right Wi-Fi router is its throughput. To do this, you'll need a router that targets at least the connection speed of your ISP. It's important to note that you won't magically achieve faster download and upload speeds by switching to a new router. Your internet speed is always limited to the slowest point of your connection, which will be the speed provided by your ISP.
To better understand this, assume you have a 100Mbps internet plan. In such a scenario, an AC1200 router would easily suffice. There's no need to spend more on an AC5000 router unless you need more antennas for better coverage, or if you want to use your wireless network to transfer files locally across the network.
Another thing to keep in mind is that the peak speeds a router claims are a combination of the different bands it uses. For example, an average AC1200 router that claims speeds of 1200 Mbps won't deliver 1200 Mbps across all bands. Instead, it will likely be limited to 300 Mbps on the 2.4 GHz channel and 867 Mbps on the 5 GHz channel. Collectively, this results in a total yield of 1200 Mbps.
4. WI-FI BANDS – DUAL-BAND VS TRI-BAND
Speaking of bands, you should know that there are three types of routers on the market. These include single-band routers, which operate only on the 2.4GHz radio. Then there are dual-band routers that support both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies. Finally, we have the new tri-band routers, which come with support for the 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz radios as well. These tri-band routers are often referred to as Wi-Fi 6E routers. For the most part, these are essentially the same Wi-Fi 6 routers but also offer the new 6GHz band.
In practice, both the 5 GHz and 6 GHz frequencies have a higher bandwidth and a much higher speed limit. On the flip side, having a higher frequency means the signal loses more power as it interacts with walls, furniture, and other obstacles. Conversely, while the 2.4 GHz band is typically capped at 300 Mbps peak speeds, it can easily penetrate walls and offers superior range.
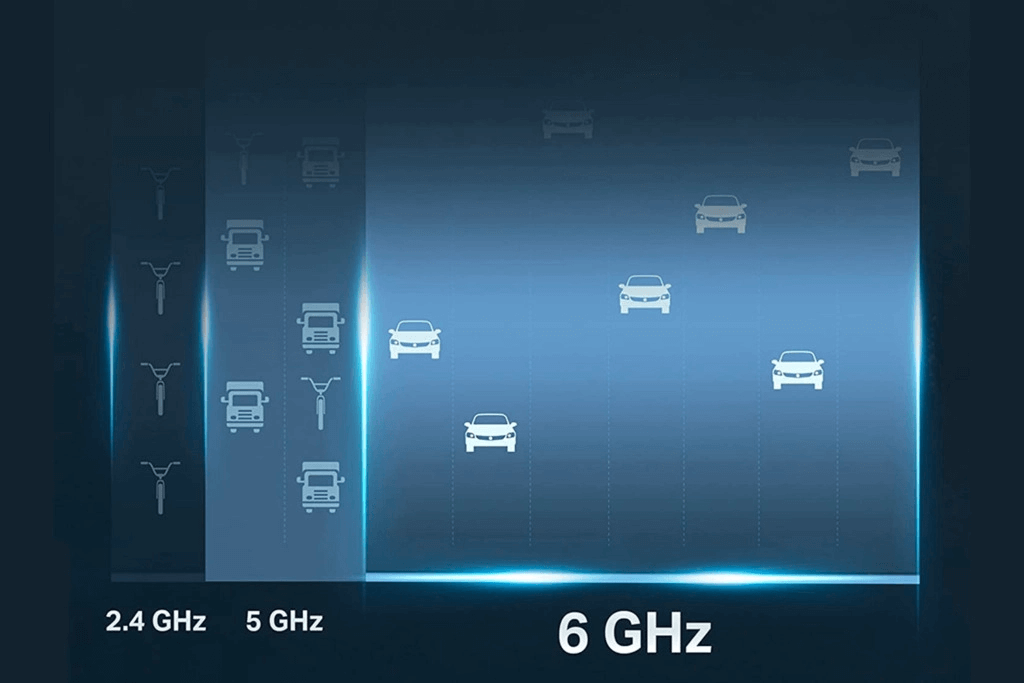
Currently, you'll either get dual-band or tri-band routers. The biggest advantage of choosing a tri-band router is that since not many other devices operate on the 6 GHz frequency, this radio has less noise. As a result, you'll get better speeds due to less congestion. However, you need to ensure that your devices also support 6 GHz connectivity.
For most people, a dual-band router is sufficient. However, if there is a lot of network congestion in your area, you're better off choosing a tri-band router.
5. Single Router VS Router Network
It's also important to consider the overall range of your Wi-Fi router before purchasing one. Of course, you'll get the best speeds when you're sitting close to the router, but you still want your Wi-Fi connection to cover every corner of your home, right? As such, there are two options to choose from: a single router or a mesh router.
Each router manufacturer highlights the coverage of their router. Alternatively, you can always refer to reviews to get a figure on the router's realistic range. For a small apartment, a single router with multiple antennas should suffice. However, if you live in a large apartment, a mesh router will serve you better.
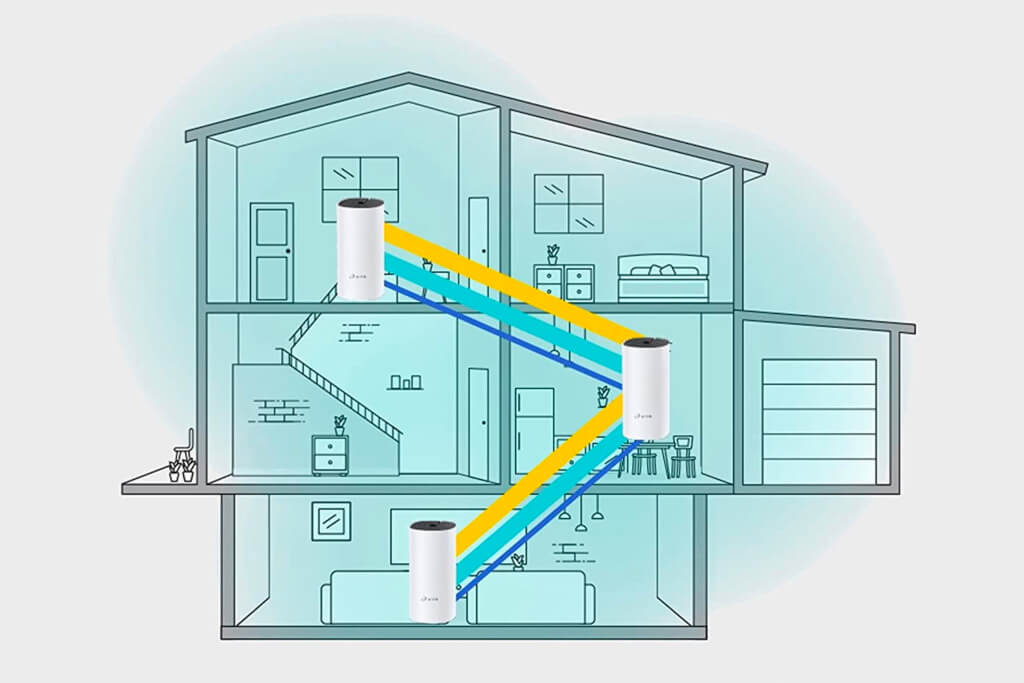
A mesh router is a special type of Wi-Fi router that uses multiple devices to provide better internet coverage throughout your home or office. It works by connecting a main device to your modem, followed by smaller devices called “nodes.” These nodes are placed in different parts of your home or office to help spread the Wi-Fi signal. Each node talks to the other nodes and to the main device to ensure the Wi-Fi network works well everywhere. As such, you shouldn’t have any areas in your home or office where the Wi-Fi connection is weak or not working at all.
If coverage is your main priority, a mesh router will always perform better than a single router. However, mesh routers are significantly more expensive, and you'll have to spend more per node. Depending on your needs and budget, you can choose between a single router or a mesh router.
6. PORTS
Sure, Wi-Fi connectivity is great, and the latest standards offer blazing speeds, too. That said, there are some devices that greatly benefit from wired Ethernet connections. Whether it's to avoid interference, achieve consistent speeds, or simply have a more reliable connection, wired connections are still the preferred choice for devices like computers, gaming consoles, and NAS drives.

As such, it's important to consider your router's Ethernet ports as well. For example, most network routers only feature a single LAN port. If you want to add your gaming console to the network as well, you'll be out of LAN ports. In such a scenario, you can opt for Ethernet adapters that add more Ethernet ports to your router.
Additionally, if you want to add storage to your network via an external hard drive or NAS drive, you need to make sure your router has USB ports as well.
7. Security standards
Aside from performance, buyers looking for Wi-Fi routers should also consider other features, including the router's security standards. Since anyone can intercept your Wi-Fi connection, it's important to protect your privacy with the best security. To this end, security standards such as WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) are now obsolete.
At the time of writing, the minimum security standard is WPA2. Although it was introduced in 2004, it remains one of the most widely used Wi-Fi security standards, thanks to its use of AES encryption. However, the newer WPA3 standard is slowly gaining traction as well. In fact, you'll find it most common on Wi-Fi 6 routers. However, there are a couple of Wi-Fi 5 routers that also offer WPA3 protection.
Simplified Wi-Fi Language
Aside from all the factors mentioned above, routers come with some other unique features as well. Some of these are extremely useful, but they can scare potential buyers away with their complex terminology. Here's a simple guide that should help you with the same when you're shortlisting a router.
What is MU-MIMO?
In traditional Wi-Fi networks, only one device can transmit data at a time, and multiple devices must wait their turn, resulting in slower data speeds. Modern Wi-Fi routers use MU-MIMO technology to improve the efficiency and speed of a wireless network. They create multiple data streams using multiple antennas and radio chains, allowing for simultaneous data transfer to different devices. This allows a Wi-Fi router to transmit data to multiple devices at the same time, resulting in faster data speeds and shorter waiting times.
What is OFDMA?
OFDMA is used to improve router data efficiency. It allows the router to send data to multiple devices at the same time, thus reducing waiting times. This is accomplished by dividing the Wi-Fi signal into smaller sub-signals called "tones." Each tone can be assigned to a different device, enabling simultaneous data transmission.
What is beamforming?
Beamforming is a router technology that focuses Wi-Fi signals directly onto connected devices. This is accomplished by using multiple antennas to pinpoint the location of the device. This results in enhanced signal strength, range, and Wi-Fi connection speed. It also helps reduce interference from other devices and obstacles such as walls.
What is Quality of Service (QOS) on WI-FI ROUTERS?
Many Wi-Fi routers have a feature called Quality of Service (QoS), which prioritizes certain types of internet traffic. For example, if you're watching a movie, QoS ensures that streaming traffic takes priority over downloading traffic. As a result, the movie will continue to play smoothly. Similarly, there are specific profiles for gaming, video calls, and more.
Frequently asked questions about how to choose Router Suitable Wi-Fi
Q1. What are the different types of routers in networks?
answer. There are several types of routers in networks, including wired routers, wireless routers, core routers, edge routers, virtual routers, distribution routers, and SOHO routers. Each type of router has a specific use case and feature set that makes it suitable for different types of networks.
Q2. Does a better router make a difference?
answer. For the most part, your internet speed will determine how fast you browse the internet. However, your router can make or break your overall connection experience. A good router can improve your internet speed, provide better coverage, reduce network congestion, and offer advanced features like parental controls, guest networks, and Quality of Service (QoS) settings. All this, while also working with the latest Wi-Fi standards and protecting your network from online threats.
Q3. How do I test my router's performance?
answer. There are several ways to test your router's performance. The first thing you can do is use a speed test tool like FAST Or Speedtest by OoklaYou can also transfer a large file between devices connected to your router to check the speed and stability of your network. Finally, we recommend using the Wi-Fi Analyzer app to check the strength of your Wi-Fi connection in different parts of your home or office. This helps identify your router's range, as well as any dead zones in your network.
Make the right choice
At the end of the day, if you're wondering what to look for in a router, this Wi-Fi router buying guide should be enough for you. By considering factors such as coverage area, frequency range, maximum data transfer rate, and security features, you can make an informed decision and select the right Wi-Fi router that meets your specific needs.
While the basic idea of "newer" is best when purchasing a Wi-Fi router, you don't necessarily need the latest technology. Make sure you know which devices you'll be connecting to your Wi-Fi connection. It's always a good idea to future-proof yourself, but only if it doesn't exceed your budget.