There are some useful graphical utilities for managing your network on macOS, but to get the real power, you'll need to use Terminal. While this may seem daunting if you're not familiar with it, you don't need to be a technical wizard to learn about your network using Terminal. Under the hood, macOS runs a variant of Unix, which means you have a wide range of networking tools available. One of the most powerful of these is nmap, which can tell you a lot about your network with just a few commands. Here's how to scan your local network using Terminal on macOS.
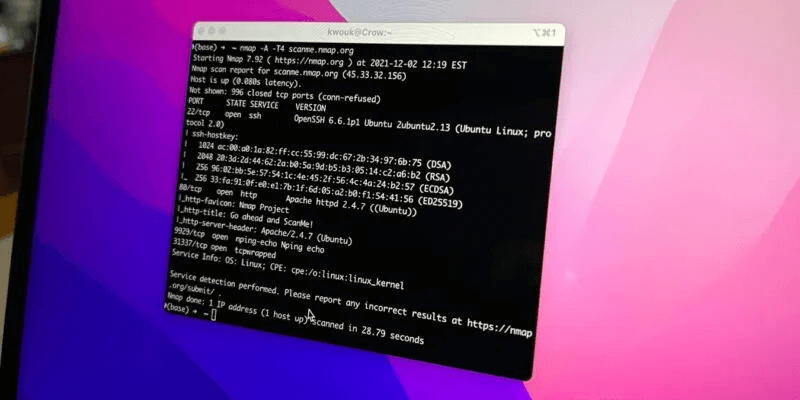
Scan open ports on your local network using nmap
nmap is the king of command-line port scanners on macOS, but you'll need to install it first.
Install nmap with Homebrew
If you have Homebrew package manager Installed, run
brew install nmap
To download and install nmap and any necessary dependencies.
Scan with nmap
Nmap is designed to scan a given hostname or network address and return a list of open ports. The name stands for Network diagram , but it's more than just a map designer.
The simplest way to run nmap is to use an IP address or a range of IP addresses as the target; replace with the appropriate IP address to scan your local network. This specific command scans the nmap tutorial test server on scanme.org.
nmap scanme.nmap.org
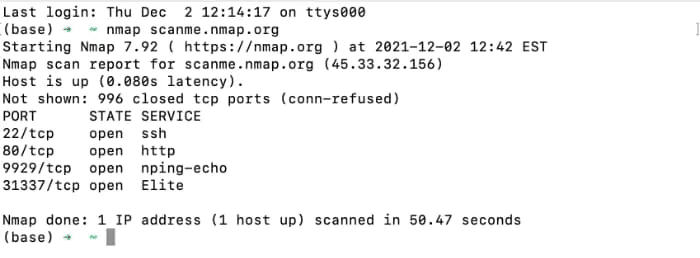
To find open ports on a range of IP addresses, use slash.
nmap 192.168.0.0/24
To find the IP addresses of your router and the various devices on your network, you can run arp Or ipconfig.
sudo nmap -A scanme.nmap.org
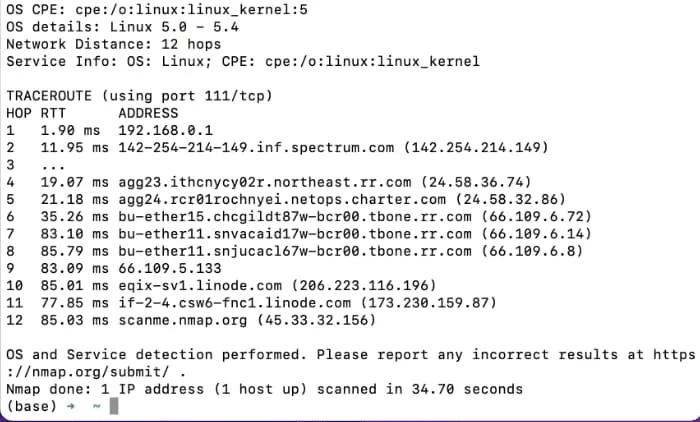
Using the tag will result in: -A to force Nmap To perform a more robust scan, return significantly more information, but transparently reveal your presence in the server logs. The flag must be turned on. -A with sudo If you can't or don't want to use the sudo command, take a look at our guide to running nmap without sudo or root.
sudo nmap -O scanme.nmap.org
This clears the specified IP address for the operating system (-O). Again, it must be run with sudo.
If you want to run Nmap More subtly, use the tag -sS:
sudo nmap -sS scanme.nmap.org
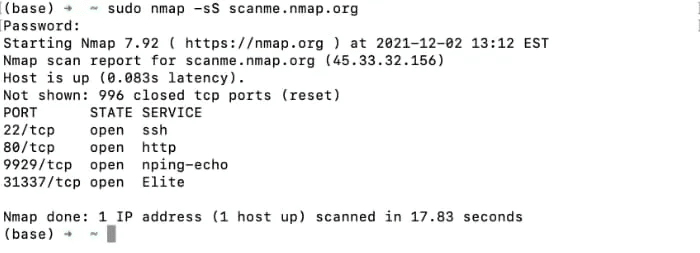
This has the effect of forcing a wipe. "half open" And sends TCP SYN packet To check if a port is open but does not respond with an ACK packet upon receiving a positive response. As such, the remote server likely does not log the scan.
The -sS flag and other scan mode switches must be enabled with sudo. For example, the -sP mode switch will scan for IP addresses, not ports, and will do something like arp below. See nmap manual page For more scanning modes.
For more extended results, add a tag. -vv Or -v3. This will trigger more levels of verbose recording, resulting in a more readable but longer standard output. Depending on what you're looking for, these flags may help you find it.
Of course, you can always point the nmap results to grep to search for specific results. If you only wanted to check port 22, for example, you could run the command below:
nmap scanme.nmap.org | grep "22/tcp"
This will not return any lines if the port is not available and will return the port status line if it is available.
Scan active IP addresses for your local network using arp
ARP scans your local network for connected devices. Because ARP is designed to create and modify address resolution protocols, it has limited tools available for scanning your network. However, it ships on every Mac and is a quick way to get specific information.
To see a list of all responsive devices currently connected to your network, open Terminal and run:
arp -a
This returns a list of all devices connected to your network, reported by IP address and MAC address.
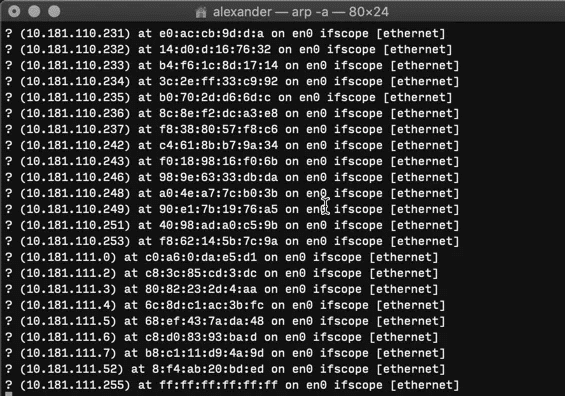
There isn't much to ARP. You can run arp -a -i en0 To get reports only from the en0 network interface, but that's it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is nmap a hacking tool?
answer. While nmap can be used for bad purposes, there is nothing about nmap that makes it hacking tool In and of itself. There's nothing wrong with using it, especially if you're using it on your own network.
Q2. Do I need to install nmap with Homebrew?
answer. No, while installing with the brew command, you can also install nmap using macOS installer from nmap website.
Q3. Is nmap only available on macOS?
answer. No. In addition to macOS, nmap is also available on Windows, Linux, and other Unix variants such as FreeBSD, Solaris, and more.
Q4. Is this all nmap can do?
answer. Covering everything nmap can do would require several articles. For more information, see nmap guide.
Network Toolkit
While nmap is certainly one of the most powerful networking tools available, it's not the only program you'll want in your toolkit. For example, ipconfig is useful for obtaining information about network interfaces, while the arp command is useful for running a quick scan of all the devices on your network.