Aside from massive camera megapixels and high refresh rate displays, the biggest trend in the smartphone world seems to be virtual RAM. Some refer to it as dynamic RAM expansion, while others call it expanded RAM. Regardless of what you call it, the idea remains the same. Allow users to use a portion of their storage space as RAM to aid multitasking. In this guide, we'll discuss how memory management works in Android and how the idea of virtual RAM differs from it. We'll try to consider whether virtual RAM is even necessary on Android or not. So let's get it.
How does memory management work on Android?
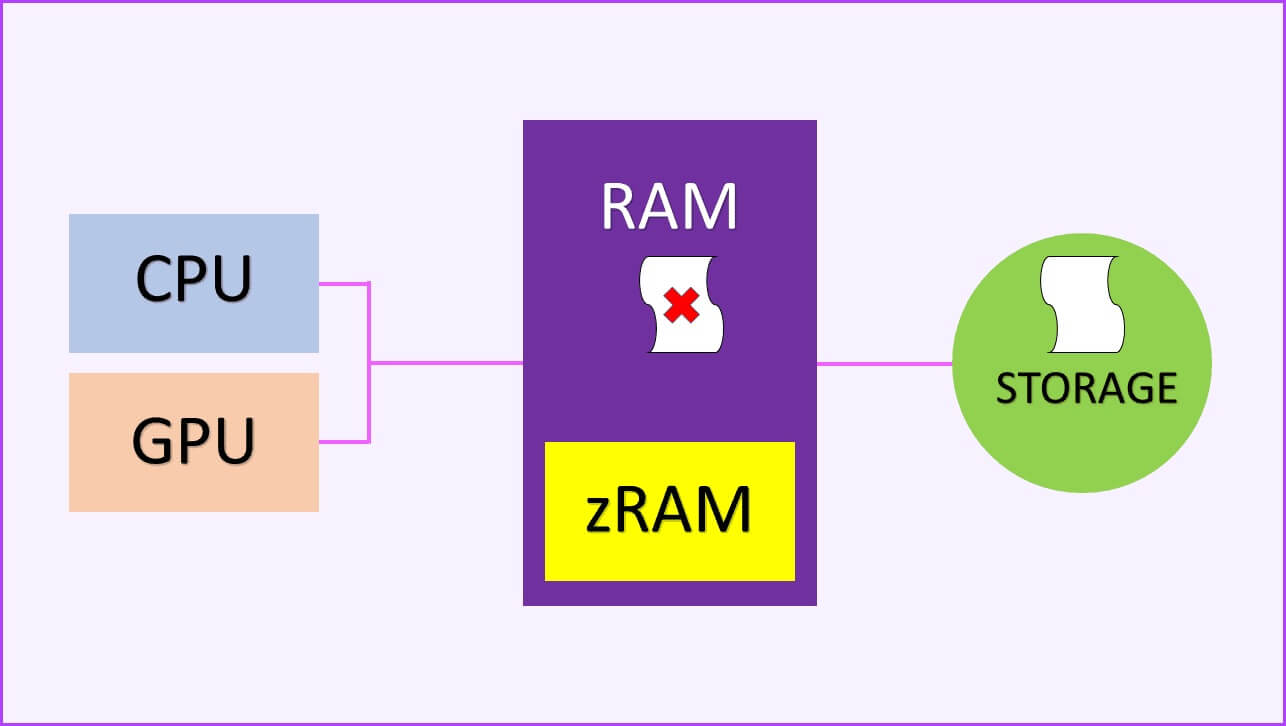
First, it's important to understand how Android manages your memory. In Android, there are three types of memory. The first is your RAM, then you have zRAM, and finally your storage. RAM is the primary memory unit that all apps run inside. Then there's onboard storage, either UFS or eMMC on budget devices. Finally, we have zRAM. Essentially, zRAM is a partition within RAM.
The idea behind zRAM is that low-priority data on RAM is compressed and stored within zRAM. Since RAM is always faster than regular storage, having compressed data within zRAM, which is part of RAM, will still be faster than accessing it from your storage device, even if you factor in the compression and decompression times.

Now that we've established the three different types of memory available to Android, let's see how the operating system handles all of that. Android uses paging techniques. The way it works is that RAM is divided into pages, with each page typically being 4 kilobytes. Whether that page is free or actively used, it combines to show used RAM and unused RAM, respectively. The kernel's job is then to convert used memory to free memory. It does this by shifting the data on those used pages to your own storage.
What is numbering and how does it work?
To understand how it works, let's understand page types. You can categorize pages into two types: clean and dirty pages. Clean pages contain an unmodified copy of the data stored in storage. Meanwhile, dirty pages contain a modified version of the data stored in storage. Now, what is this modified and unmodified version? Let's call it dynamic memory usage.
Unmodified copies are static data, while modified copies are dynamic data that changes every second. Android can flush clean pages as needed since they don't access resources dynamically. This helps free up RAM and make more available. This may sound very technical, so let's make it easier to understand how to use them in real-world applications.
Suppose you opened Twitter , browse your feed, and then switch to something else. Twitter is still in your RAM. But if you don't open it for a while, its priority decreases. Later, if you launch something new, Android will have to free up the memory Twitter was using. So what it does is it shifts its values and data to storage, giving you free space. This is why when you launch Twitter again, it will first show you the timeline it hibernated on, then refresh. The same goes for Facebook Or Reddit Or similar apps like Calculator or Notes. These apps use clean slates, where a copy of their data is permanently saved within your storage.
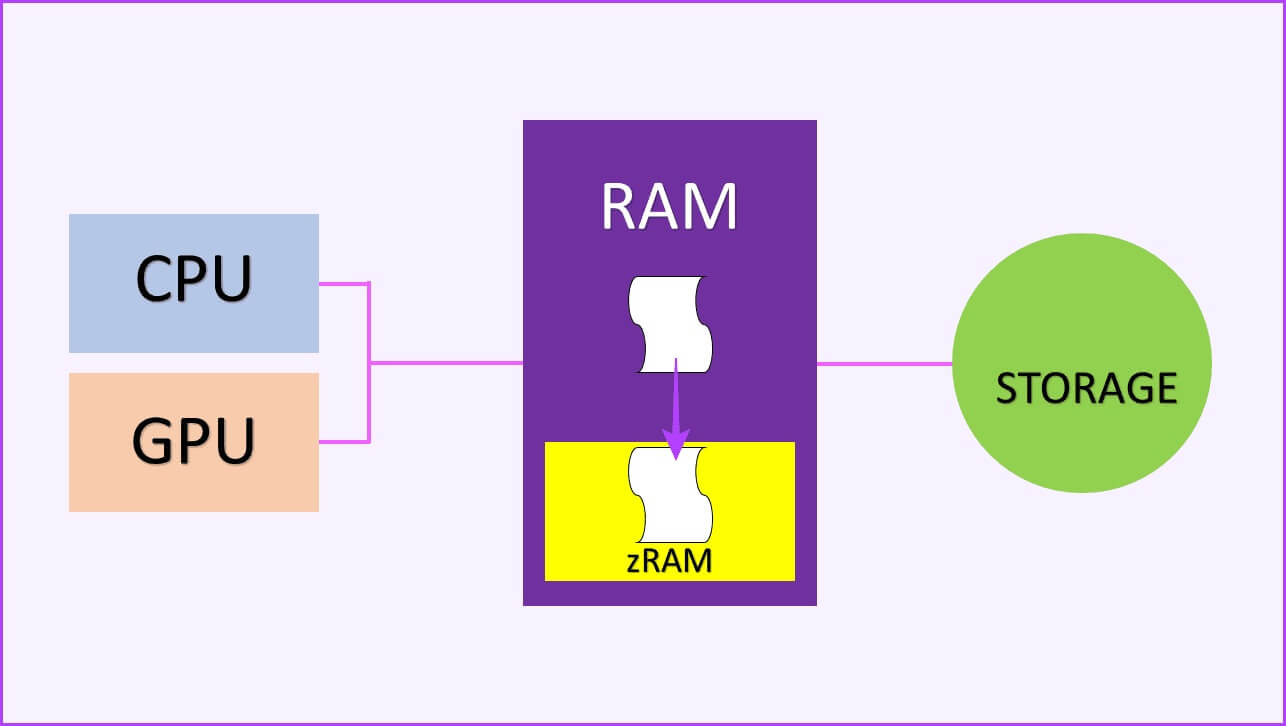
Now, for dirty pages, keep in mind: Spotify Or any music player. You can play some music within the player and then play it in the background without opening the app. However, the system cannot close it because it dynamically uses your memory. As a result, Android compresses the app and shifts it to zRAM when it needs more free RAM.
What is virtual RAM?
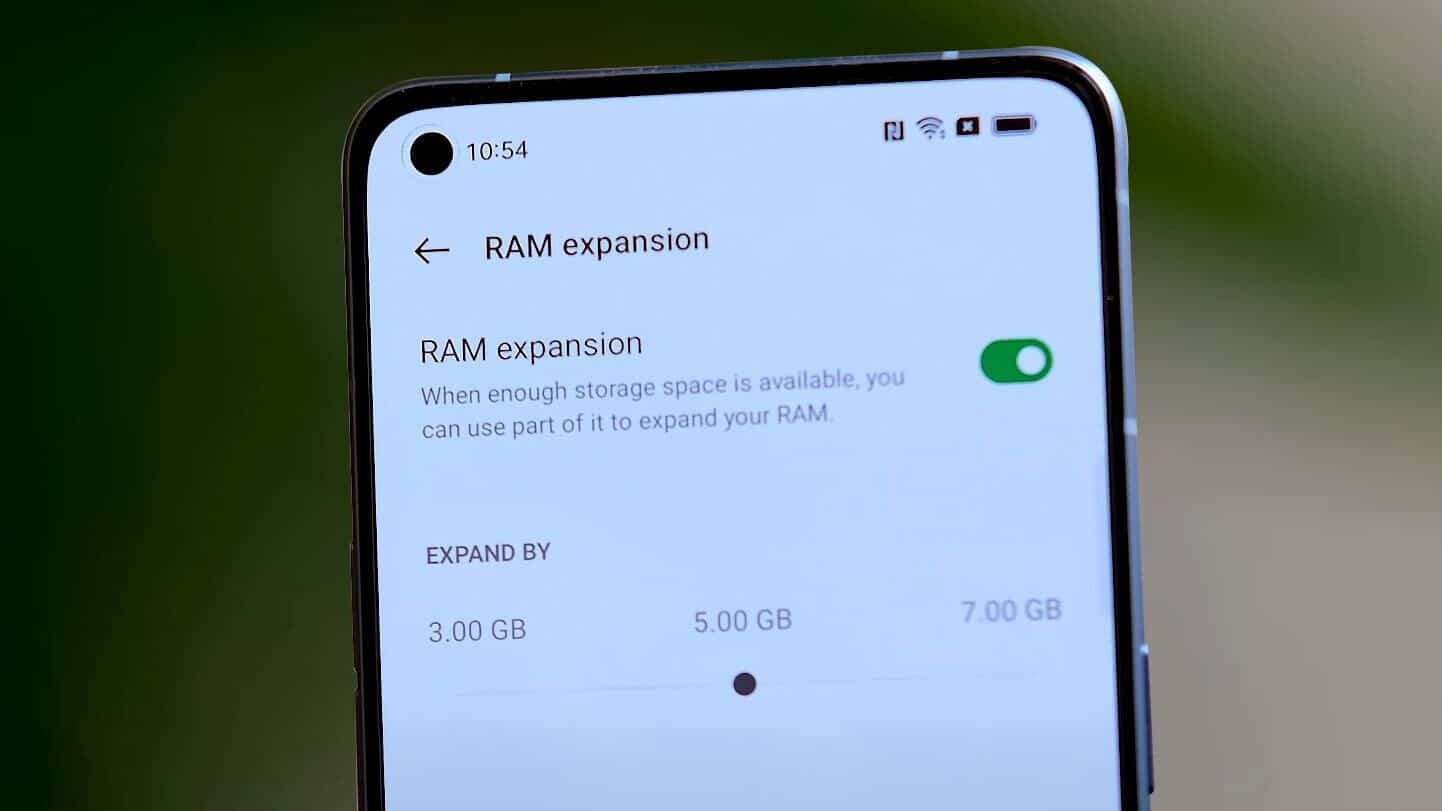
Now that you know how Android manages memory, you might be wondering—where does virtual RAM come in? Remember how we said that zRAM is also part of RAM? The way virtual RAM works is that it creates a swap partition on your storage space and uses it as additional zRAM.
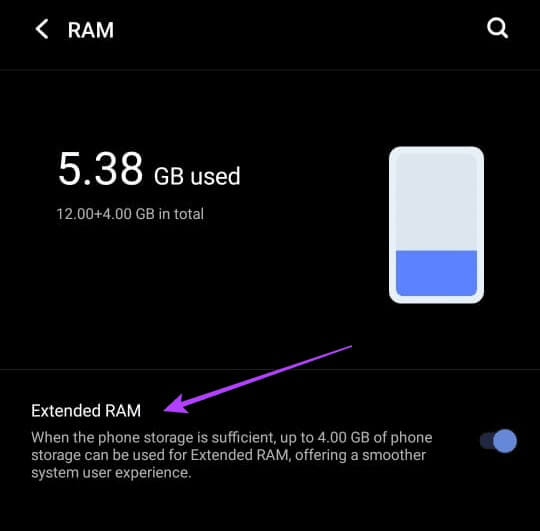
Because zRAM is stored solely on your RAM, there's a limit to the number of pages you can compress and store there. Using a swap partition, you can use your storage space as additional zRAM to compress and convert applications, while freeing up space in your physical RAM.
This feature is new.
So, is this all new? Well, not really. Linux has used swap partitions since the beginning. For Android, custom kernel users use their SD cards to create additional swap partitions to improve memory management.
As such, manufacturers are giving you the same feature baked into their Android skins. However, this begs the question: if the feature is so useful, why isn't it part of the Android source code?
Virtual RAM is good or bad
The answer lies in the basic workings of virtual RAM itself. While the feature allows you to run more apps on your device by compressing hibernated apps and transferring them to your storage, it does more harm than good. Since swap partitions primarily store active apps, there's a higher read and write throughput.
This works well for traditional storage, but flash memory has a limited number of read and write operations. Therefore, using SWAP or virtual RAM reduces the lifespan of your device's storage.
This is also well marked in Android Developer Page“On Android, storage isn’t used for swap space as it is in other Linux implementations, where frequent writes can wear out this memory and shorten the life of the storage medium.” Another example of this is found on the new Apple M1 MacBooks. These devices use a swap partition on Apple’s SSDs, which users have complained about a lot.
Is Virtual RAM Important and Should You Use It?
Basically, it all depends on how you define multitasking. If you're switching between two or three active apps, virtual RAM is definitely helping. But if you're constantly switching between five or six actively active apps, virtual RAM won't do anything because it will keep changing apps.
Essentially, virtual RAM gives you more RAM available to run apps. However, it comes at the expense of your storage. If you plan to continue using your device for more than two years, we believe using virtual RAM may not make much sense.